PAM Chemicals for Effective Water Treatment Solutions and Processes
PAM Chemical for Water Treatment An Overview
Polyacrylamide (PAM) is a versatile chemical that has gained notable attention in the field of water treatment due to its effective flocculating and coagulating properties. PAM is a water-soluble polymer that can improve the efficiency of various water treatment processes. Its application spans a wide range of industries, from municipal wastewater treatment to industrial processes and even agricultural practices. Understanding the characteristics and benefits of PAM can illuminate its importance in water treatment solutions.
What is PAM?
Polyacrylamide is a synthetic polymer made from acrylamide monomers. It has the unique ability to enhance the settling of solids, thereby clarifying water. PAM is available in several forms, including anionic, cationic, and nonionic variants, which can be selected according to the specific requirements of the treatment process. Each type of PAM has different charge characteristics that determine its effectiveness in various water treatment scenarios.
Mechanism of Action
The primary function of PAM in water treatment involves the aggregation of suspended particles, making it easier for them to settle or be filtered out. When PAM is added to water, it interacts with negatively charged particles, neutralizing their charges and promoting flocculation. This process results in larger aggregates (or flocs) that can be easily removed through sedimentation or filtration.
In municipal wastewater treatment, for example, PAM is commonly used in the clarification process. The addition of PAM can significantly reduce the turbidity of water, leading to cleaner effluent and an overall improvement in water quality. Furthermore, PAM assists in the reduction of sludge volume, making the overall treatment process more efficient.
Applications of PAM in Water Treatment
1. Municipal Wastewater Treatment PAM is extensively used in municipal sewage treatment plants to enhance the removal of organic matter and suspended solids. By improving the settling characteristics of the sludge, PAM helps ensure that wastewater can be treated effectively and safely discharged.
2. Industrial Water Treatment In various industries, such as paper manufacturing, mining, and oil and gas, PAM plays a crucial role in managing water quality. In these applications, PAM can aid in the removal of solids from process water, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations and enhancing operational efficiency.
pam chemical for water treatment
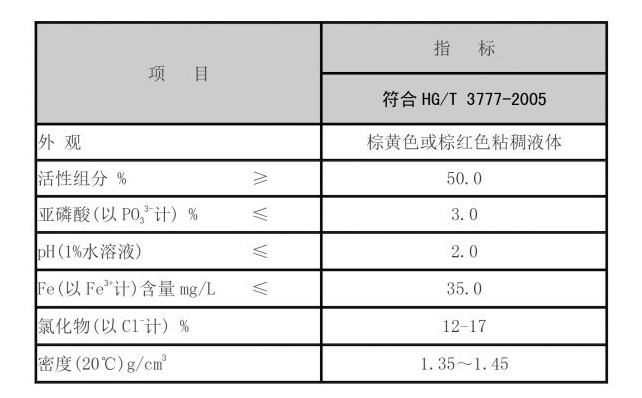
3. Drinking Water Treatment PAM can also be utilized in the treatment of drinking water, where it aids in the removal of contaminants and particulates. The use of PAM can improve the efficiency of sand filters and other clarification processes, leading to cleaner drinking water.
4. Agricultural Applications In agriculture, PAM is used to enhance irrigation efficiency. When applied to soil, PAM can improve water retention and reduce soil erosion. This application not only conserves water but also fosters better crop yields.
Advantages of Using PAM
The use of PAM in water treatment brings numerous advantages
- Increased Efficiency PAM enhances coagulation and flocculation processes, leading to faster and more efficient removal of suspended solids. - Cost-Effectiveness By reducing the volume of sludge produced and improving the treatment processes, PAM can lower operational costs in wastewater treatment facilities. - Versatility With various forms available, PAM can be customized for a wide range of applications, catering to specific water treatment needs. - Environmental Benefits Efficient water treatment processes contribute to the protection of water bodies and ecosystems by minimizing pollution and promoting sustainability.
Considerations and Safety
While PAM is generally considered safe for use in water treatment, it is essential to handle it appropriately, given that acrylamide is a known neurotoxin. Adhering to safety protocols during the handling and application of PAM is crucial. Regulatory guidelines must be followed to ensure that the use of PAM does not pose risks to human health or the environment.
Conclusion
PAM has emerged as a vital component in the toolkit for water treatment professionals. Its effectiveness in enhancing the coagulation and flocculation processes makes it an invaluable substance in municipal and industrial applications. As the demand for cleaner water and sustainable practices continues to grow, PAM will likely play an increasingly important role in advancing water treatment technologies, helping to ensure safe water for various purposes while promoting environmental sustainability.
-
Pbtc Scale InhibitorPBTC: A Scale Protector for Industrial Water TreatmentNewsAug.05,2025
-
Organic Phosphonate: An Efficient Defender in the Field of Scale InhibitionNewsAug.05,2025
-
Hydrolyzed Polymaleic Anhydride: Green Pioneer in Scale Inhibition FieldNewsAug.05,2025
-
PAPEMP Polyamino Polyether Methylene Phosphonic Acid For SaleNewsAug.05,2025
-
Flocculant Water Treatment: A Pioneer in Purification in the Field of Water TreatmentNewsAug.05,2025
-
Benzyl Isothiazolinone: An Efficient and Broad-Spectrum Antibacterial Protective GuardNewsAug.05,2025





