polyacrylamide polymer
Understanding Polyacrylamide Polymer Applications and Benefits
Polyacrylamide (PAM) is a versatile synthetic polymer widely used across various industries due to its unique properties and applications. It is produced through the polymerization of acrylamide monomers, resulting in a polymer that can be tailored to meet specific needs by adjusting its molecular weight and structure. PAM is utilized primarily in water treatment, soil conditioning, and various industrial processes.
Water Treatment Applications
One of the most significant applications of polyacrylamide polymers is in water treatment. PAM serves as a flocculant, helping to aggregate suspended particles in water, facilitating their removal. This function is crucial in municipal water treatment facilities, where achieving high water clarity and quality is essential for public health. By improving coagulation and sedimentation, PAM enhances the efficiency of filtration processes, making it a valuable tool for managing wastewater and drinking water treatment.
Agricultural Uses
In agriculture, polyacrylamide polymers play a critical role in enhancing soil quality and water retention. When applied to soil, PAM can reduce erosion, enhance nutrient retention, and improve water infiltration. This is particularly beneficial in arid and semi-arid regions, where water conservation is paramount. The ability of PAM to form a gel-like substance when hydrated helps bind soil particles together, reducing runoff and promoting sustainable land management practices.
Industrial Applications
polyacrylamide polymer
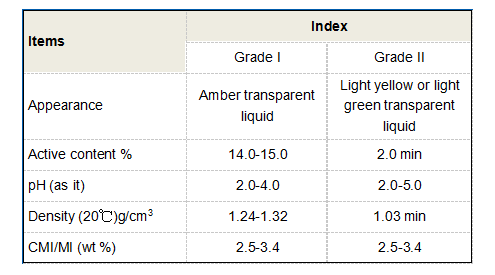
Beyond environmental uses, polyacrylamide is extensively implemented in several industrial processes. For instance, in the oil and gas industry, PAM is used in enhanced oil recovery (EOR) processes to improve the efficiency of oil extraction. By increasing the viscosity of water injected into reservoirs, PAM helps to sweep more oil toward production wells. Additionally, PAM finds applications in papermaking, textiles, and mining, where it aids in the thickening and binding of materials.
Types of Polyacrylamide
Polyacrylamide can be categorized into anionic, cationic, and non-ionic types, depending on the charge of the polymer chains. Anionic polyacrylamides are primarily used in water treatment applications where negative charges are beneficial for flocculation. Cationic polyacrylamides, on the other hand, are effective in applications where a positive charge is needed to attract negatively charged particles. Non-ionic polyacrylamides are utilized for their versatility across various applications without imparting a charge.
Environmental Considerations
While the benefits of polyacrylamide are significant, it's essential to consider its environmental impact. When used appropriately and in regulated amounts, PAM is generally considered safe. However, the potential toxicity of acrylamide—a key monomer in PAM production—has raised concerns, leading to strict regulations in many areas regarding its use. Therefore, ongoing research and development aim to find safer alternatives and improve the environmental footprint of polyacrylamide applications.
In conclusion, polyacrylamide is a crucial polymer with diverse applications ranging from water treatment to agriculture and industry. Its ability to enhance efficiency and promote sustainable practices makes it an invaluable resource in modern applications, underscoring the importance of responsible usage and continuous innovation in this field.
-
The Power of Isothiazolinones in Modern ApplicationsNewsMay.08,2025
-
Flocculants in Water TreatmentNewsMay.08,2025
-
Flocculants and Chemical Solutions: What You Need to KnowNewsMay.08,2025
-
Flocculants and Chemical Solutions: A Growing IndustryNewsMay.08,2025
-
Essential Chemicals: Polymaleic Anhydride and MoreNewsMay.08,2025
-
Acrylic Polymers: Essential Solutions for IndustryNewsMay.08,2025





