polyacrylamide water treatment
The Role of Polyacrylamide in Water Treatment
Water scarcity and pollution are two significant challenges faced by our world today. As industries expand and urbanization progresses, the need for effective water treatment solutions becomes more critical. Among various chemicals used for water treatment, polyacrylamide stands out due to its unique properties and versatility. This article delves into the significance of polyacrylamide in water treatment processes, its mechanism, advantages, applications, and potential environmental impact.
Understanding Polyacrylamide
Polyacrylamide (PAM) is a synthetic polymer derived from acrylamide monomers. Characterized by its high molecular weight and ability to form gels, polyacrylamide is often utilized as a flocculant, a substance that promotes the agglomeration of particles in water. Depending on its formulation, polyacrylamide can be anionic, cationic, or non-ionic, each serving distinct roles in water treatment processes.
Mechanism of Action
The primary function of polyacrylamide in water treatment is to enhance the settling of suspended solids. The charged groups on the polymer chains interact with oppositely charged particles, creating larger aggregates or flocs. This process facilitates the removal of these particles from water, leading to clearer, cleaner water. The efficiency of polyacrylamide as a flocculant is particularly noteworthy in various environments, from municipal wastewater treatment plants to industrial effluent management systems.
Advantages of Polyacrylamide in Water Treatment
1. Enhanced Settling Rates By promoting floc formation, polyacrylamide significantly increases the settling rates of suspended solids. This leads to faster processing times and reduces the overall cost of water treatment.
2. Versatility The adaptability of polyacrylamide allows it to be utilized in various applications, including sedimentation, clarification, and dewatering processes across different industries.
3. Improved Water Quality Water treated with polyacrylamide exhibits improved clarity and reduced turbidity, making it more suitable for discharge into natural water bodies or for reuse in irrigation and industrial processes.
4. Lower Chemical Usage Polyacrylamide can reduce the need for other chemicals in the treatment process, which not only cuts costs but also mitigates potential environmental impacts.
polyacrylamide water treatment
Applications in Water Treatment
Polyacrylamide is widely used in various sectors, including
- Municipal Water Treatment It is employed to clarify drinking water and treat wastewater, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
- Industrial Effluent Management Industries, especially those in manufacturing, mining, and food processing, utilize polyacrylamide to manage wastewater and recover valuable materials.
- Agricultural Practices PAM is used to improve water retention in soil, reduce erosion, and enhance irrigation efficiency, contributing to more sustainable agricultural practices.
Environmental Impact and Considerations
Despite its numerous benefits, the use of polyacrylamide in water treatment is not without concerns. One major issue is the potential toxicity of acrylamide, a known neurotoxin, when exposed to certain conditions or high concentrations. Regulatory agencies emphasize the importance of proper handling and dosage of polyacrylamide to minimize risks. Furthermore, while some formulations are biodegradable, the long-term environmental effects of synthetic polymers remain an area of ongoing research.
Conclusion
Polyacrylamide has emerged as a crucial component in modern water treatment practices, addressing pressing issues of water quality and availability. Its ability to enhance settling rates, improve water clarity, and reduce chemical reliance makes it an attractive option for municipalities and industries alike. However, as with any chemical agent, responsible usage and thorough understanding of its environmental implications are essential. With continued research and development, polyacrylamide could play an even more significant role in achieving sustainable water management in the future. As we navigate the challenges of an increasingly water-scarce world, innovations in water treatment will be pivotal in safeguarding our most vital resource.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
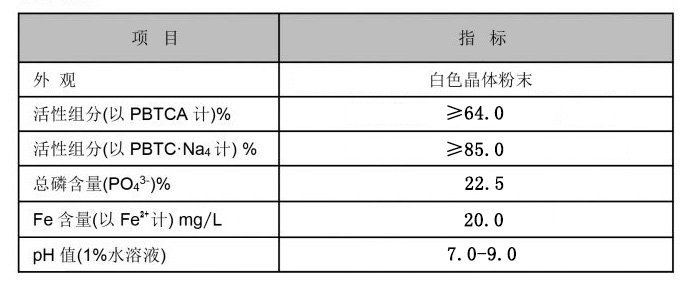
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





