2월 . 14, 2025 20:34
Back to list
PAM Poly Acrylamide
Polyacrylamide (PAM) has emerged as a versatile polymer with a myriad of applications across various industries, from water treatment to agriculture. This article provides an in-depth exploration of polyacrylamide, detailing its functionality, applications, and benefits, while also emphasizing the need for responsible usage and proper safety measures.
With great authority comes the responsibility to ensure that these polymers are used safely. Despite its myriad benefits, polyacrylamide must be handled with care due to the potential risks associated with acrylamide, a monomer that can have toxic effects. Regulatory compliance is critical; therefore, rigorous testing and monitoring of PAM applications are essential to safeguard human health and the environment. It is imperative for industry stakeholders to adhere to safety guidelines issued by authoritative bodies such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), to prevent exposure and promote safe handling practices. Trustworthiness in the use of polyacrylamide stems from transparency and accountability in its production and usage. Manufacturers are expected to provide comprehensive material safety data sheets (MSDS) and ensure that their products meet international standards of quality and safety. Users, on the other hand, are encouraged to undertake routine training and awareness programs to remain informed about best practices regarding polyacrylamide use. In conclusion, polyacrylamide is a multifaceted compound that holds significant promise across several domains. Its utility in improving water quality, enhancing agricultural yield, and facilitating industrial processes underscores its importance in sustainable development. However, the onus is on manufacturers, researchers, and users to harness this compound responsibly, ensuring that its benefits are maximized while mitigating any potential risks. As research progresses, the future of polyacrylamide lies in innovation and sustainable practices that align with the evolving needs of industries and environmental conservation efforts.
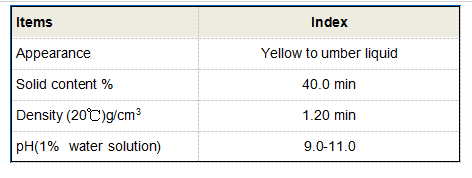

With great authority comes the responsibility to ensure that these polymers are used safely. Despite its myriad benefits, polyacrylamide must be handled with care due to the potential risks associated with acrylamide, a monomer that can have toxic effects. Regulatory compliance is critical; therefore, rigorous testing and monitoring of PAM applications are essential to safeguard human health and the environment. It is imperative for industry stakeholders to adhere to safety guidelines issued by authoritative bodies such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), to prevent exposure and promote safe handling practices. Trustworthiness in the use of polyacrylamide stems from transparency and accountability in its production and usage. Manufacturers are expected to provide comprehensive material safety data sheets (MSDS) and ensure that their products meet international standards of quality and safety. Users, on the other hand, are encouraged to undertake routine training and awareness programs to remain informed about best practices regarding polyacrylamide use. In conclusion, polyacrylamide is a multifaceted compound that holds significant promise across several domains. Its utility in improving water quality, enhancing agricultural yield, and facilitating industrial processes underscores its importance in sustainable development. However, the onus is on manufacturers, researchers, and users to harness this compound responsibly, ensuring that its benefits are maximized while mitigating any potential risks. As research progresses, the future of polyacrylamide lies in innovation and sustainable practices that align with the evolving needs of industries and environmental conservation efforts.
Share
Next:
Latest news
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





