sodium hedp 钠hedp
Understanding Sodium HEDP Benefits and Applications
Sodium Hydroxyethylidene Diphosphonic Acid, commonly referred to as sodium HEDP, is a phosphonic acid derivative that has garnered significant attention due to its extensive applications in various industries. As a chelating agent, sodium HEDP is particularly notable for its ability to bind with metal ions, which plays a crucial role in several industrial processes.
Chemical Properties and Structure
Sodium HEDP is characterized by its unique chemical structure, where the hydroxyethyl group enhances its solubility in water. This property makes sodium HEDP highly effective in applications where interaction with aqueous solutions is necessary. The compound is often supplied as a sodium salt, which further contributes to its stability and efficacy in different environments.
Industrial Applications
Understanding Sodium HEDP Benefits and Applications
In the oil and gas industry, sodium HEDP is employed to mitigate the effects of mineral deposits that can impair extraction processes. The compound helps maintain fluidity in drilling operations and prevents the buildup of scale in pipelines, thus optimizing extraction efficiency and reducing maintenance costs.
sodium hedp 钠hedp
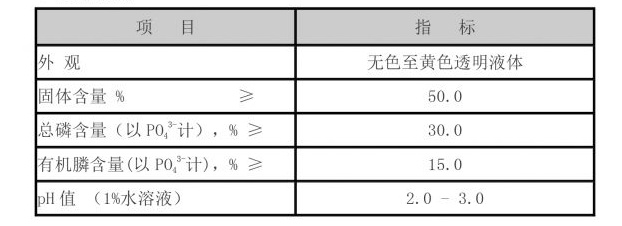
Additionally, sodium HEDP is utilized in the manufacturing of detergents and cleaning agents. Its ability to sequester metal ions not only enhances the cleaning power of these products but also improves their stability and effectiveness in hard water conditions. Consequently, sodium HEDP has become a vital component in household and industrial cleaning formulations.
Agricultural Uses
Sodium HEDP also finds applications in agriculture. It is used as an additive in fertilizers to enhance nutrient uptake by plants. The chelating properties of sodium HEDP enable it to bind essential micronutrients, making them more bioavailable to plants. As a result, the incorporation of sodium HEDP in agricultural practices can lead to improved crop yields and healthier plants.
Environmental Considerations
While sodium HEDP is highly beneficial in various applications, it is essential to consider its environmental impact. The compound is generally regarded as low in toxicity when used appropriately. However, like any chemical agent, it necessitates responsible handling and disposal to prevent potential harm to aquatic ecosystems. Research and development efforts continue to focus on minimizing the environmental footprint of sodium HEDP while maximizing its benefits across different sectors.
Conclusion
In conclusion, sodium HEDP is a versatile and effective chelating agent with a wide range of applications spanning water treatment, oil and gas extraction, cleaning products, and agriculture. Its unique chemical properties not only enhance industrial processes but also contribute positively to agricultural productivity. As industries continue to seek sustainable and efficient solutions, sodium HEDP is likely to maintain its significance in various fields. The ongoing research into its applications and environmental impact will further solidify its role as a crucial ingredient in modern industrial and agricultural practices.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





