Polyhalogenated Aluminum Chloride as an Effective Coagulant in Water Treatment Processes
The Role of Poly-Aluminum Chloride Coagulant in Water Treatment
Water is a vital resource for life, and its cleanliness is essential for human health and the environment. To ensure that water is free from contaminants, various treatment methods are employed, among which the use of coagulants like poly-aluminum chloride (PAC) has gained prominence. PAC is a versatile coagulant that plays a crucial role in the removal of suspended solids, organic materials, and other impurities from water.
What is Poly-Aluminum Chloride?
Poly-aluminum chloride is an inorganic polymer that serves as an effective coagulant in water treatment processes. It is synthesized by the hydrolysis of aluminum chloride in the presence of a base, resulting in a compound that is more effective than traditional aluminum sulfate. Its chemical formula varies depending on its degree of polymerization, but it generally has a high aluminum content and is characterized by a positive charge, making it efficient in neutralizing the negative charges of suspended particles in water.
Mechanism of Action
The coagulation process involves the aggregation of fine particles into larger flocs, which can then be easily removed from the water through sedimentation or filtration. When PAC is added to water, it undergoes hydrolysis, releasing aluminum ions. These positively charged ions attract negatively charged particles, such as colloids and silt, causing them to clump together. This aggregation process is crucial in producing larger particles that can settle more quickly and be removed effectively.
Advantages of Using PAC
One of the significant advantages of poly-aluminum chloride over traditional coagulants is its efficiency at lower dosages. PAC requires less quantity to achieve the same level of turbidity removal compared to aluminum sulfate, which leads to reduced operational costs and less sludge production. Furthermore, PAC can perform well across a wide range of pH levels, making it suitable for various types of water sources.
polyaluminum chloride coagulant
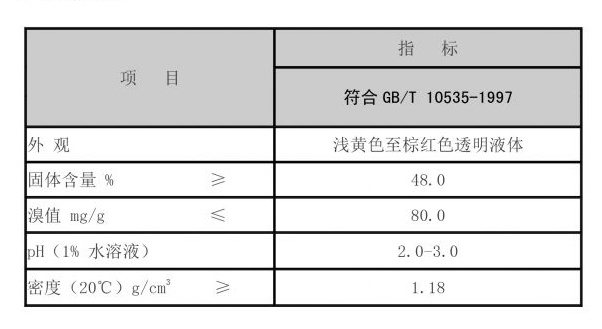
Another notable benefit is the improved settling characteristics of the flocs produced when using PAC. The larger and denser flocs typically result in quicker settling, enhancing the overall efficiency of water treatment facilities. This property is particularly valuable in systems where space constraints limit the sedimentation area.
Environmental Considerations
The use of poly-aluminum chloride also has environmental benefits. Conventional coagulants can sometimes lead to the formation of excessive sludge that can pose disposal challenges. PAC, with its improved settling ability, minimizes sludge volume and creates a more manageable waste stream. Moreover, the use of PAC contributes to the reduction of residual aluminum in treated water, addressing environmental concerns associated with aluminum toxicity.
Applications Beyond Water Treatment
Beyond its primary application in municipal water treatment, PAC is also utilized in industrial processes, such as the treatment of wastewater from various sectors, including food processing, paper manufacturing, and mining. Its efficiency in removing contaminants makes it an indispensable tool in maintaining water quality standards across diverse applications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, poly-aluminum chloride serves as a powerful and efficient coagulant in water treatment that addresses the challenges of sedimentation and turbidity removal effectively. Its advantages over traditional coagulants, coupled with its versatility and environmental friendliness, make PAC a popular choice in both municipal and industrial settings. As the world continues to grapple with water quality issues, the role of coagulants like poly-aluminum chloride remains crucial in ensuring the sustainability and safety of this essential resource.
-
Understanding Acrylic Homopolymers and Their ApplicationsNewsApr.01,2025
-
The Emerging Importance of Polyaspartic AcidNewsApr.01,2025
-
Poly Aluminum Chloride and Polyacrylamide: Key Players in Water TreatmentNewsApr.01,2025
-
Flocculants for Water TreatmentNewsApr.01,2025
-
Essential Solutions for Water Treatment and PurificationNewsApr.01,2025
-
Chemical Solutions for Advanced IndustriesNewsApr.01,2025





