Enhancing Water Purification Processes Using Poly Aluminum Chloride for Effective Treatment Solutions
The Role of Poly Aluminum Chloride in Water Treatment
Water treatment is an essential process that ensures the provision of clean and safe drinking water. Among the various coagulants and flocculants used in this process, Poly Aluminum Chloride (PAC) has emerged as a highly effective solution. This compound is a type of inorganic polymer that is widely utilized in the treatment of drinking water, wastewater, and industrial effluents. Its unique chemical properties and performance make it an indispensable tool in maintaining water quality.
What is Poly Aluminum Chloride?
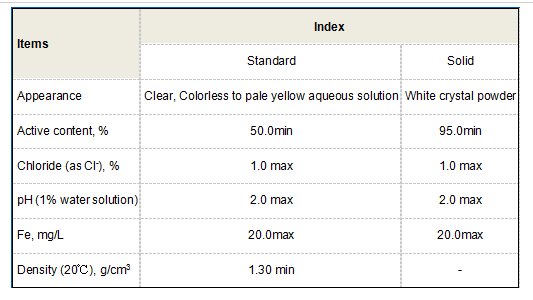
Poly Aluminum Chloride is a versatile chemical compound formulated from aluminum chloride and sodium hydroxide. It comes in liquid and dry forms, with varying degrees of basicity. The basicity level indicates the ratio of hydroxide ions to aluminum ions, impacting the compound’s effectiveness in coagulation processes. PAC is recognized for its superior coagulation capability compared to traditional coagulants like aluminum sulfate, which allows for more efficient removal of suspended solids and impurities from water.
Mechanism of Action
The primary function of PAC in water treatment is to aggregate fine particles and impurities through a process known as coagulation. Upon application, PAC dissociates in water, releasing aluminum ions that neutralize the negative charges of suspended particles. This neutralization encourages the particles to clump together, forming larger aggregates known as flocs. These flocs are subsequently removed through sedimentation or filtration, leading to clearer and cleaner water.
The effectiveness of PAC as a coagulant is influenced by several factors, including pH, temperature, and the presence of other substances in the water. Typically, PAC operates effectively in a wide range of pH levels (approximately 6 to 8), making it suitable for various water sources. Moreover, PAC can function efficiently even in low concentrations, which makes it a cost-effective option for water treatment facilities.
Advantages of Using PAC
poly aluminum chloride water treatment
The use of Poly Aluminum Chloride in water treatment offers numerous advantages. Firstly, PAC can produce higher rates of settlement and clearer supernatants compared to traditional coagulants. This rapid settling reduces the time and energy needed for the clarification process, making treatment plants more efficient.
Secondly, PAC generates less sludge with better dewaterability. The generated sludge is often less bulky, resulting in lower disposal costs and a reduced environmental footprint. Additionally, the presence of aluminum in PAC helps in the aluminum residual levels in treated water, which can enhance taste and reduce turbidity levels.
Furthermore, PAC has been found to effectively remove not only suspended solids but also natural organic matter, color, and some heavy metals. This enhances the overall quality of the treated water, meeting stringent regulatory standards for potable water.
Environmental Considerations
While PAC is a powerful coagulant, its environmental implications warrant attention. The aluminum residuals in treated water must be monitored to ensure they remain within safe limits, as excessive aluminum can have adverse health effects. However, when applied correctly, PAC is considered a safe and advantageous choice compared to certain alternatives.
Conclusion
Poly Aluminum Chloride represents a significant advancement in water treatment technology. Its efficiency in coagulation, rapid settling, reduced sludge production, and ability to remove a wide range of contaminants make it a preferred choice for water treatment facilities worldwide. As communities strive to provide safe drinking water while managing environmental impact, PAC continues to play a crucial role in achieving these goals. With ongoing research and technological advancements, the applications of PAC in water treatment are likely to expand, contributing further to global water quality initiatives.
-
The Power of Isothiazolinones in Modern ApplicationsNewsMay.08,2025
-
Flocculants in Water TreatmentNewsMay.08,2025
-
Flocculants and Chemical Solutions: What You Need to KnowNewsMay.08,2025
-
Flocculants and Chemical Solutions: A Growing IndustryNewsMay.08,2025
-
Essential Chemicals: Polymaleic Anhydride and MoreNewsMay.08,2025
-
Acrylic Polymers: Essential Solutions for IndustryNewsMay.08,2025





