Polyacrylamide Applications and Methods in Modern Biochemical Research and Industrial Processes
Understanding Polyacrylamide Properties, Applications, and Environmental Impact
Polyacrylamide (PAM) is a synthetic polymer that has garnered significant attention in various fields due to its diverse range of properties and applications. Composed of acrylamide monomers, this high molecular weight polymer exhibits unique characteristics such as water solubility, gel-forming capabilities, and excellent adhesion properties. These features make polyacrylamide a versatile material widely used in industries ranging from agriculture to wastewater treatment.
Understanding Polyacrylamide Properties, Applications, and Environmental Impact
In addition to its agricultural uses, polyacrylamide is extensively utilized in the treatment of wastewater. As a flocculant, PAM promotes the aggregation of suspended particles in water, facilitating their removal during the filtration process. Its application in wastewater treatment not only improves water clarity but also enhances the efficiency of the overall treatment process. By binding to contaminants, polyacrylamide helps in separating solids from liquids, making it an essential component in municipal and industrial wastewater management systems.
polyacrylamide pdf
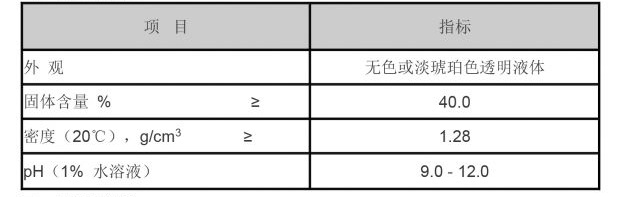
The versatility of polyacrylamide extends to the biomedical field as well. Its biocompatibility, non-toxic nature, and ability to form hydrogels make PAM suitable for a range of medical applications, including drug delivery, wound healing, and tissue engineering. Researchers are exploring its potential in creating controlled release systems for pharmaceuticals, allowing for sustained and targeted delivery. Furthermore, polyacrylamide-based hydrogels can be engineered to mimic the properties of natural tissues, offering exciting possibilities for regenerative medicine.
Despite its numerous advantages, concerns have arisen regarding the environmental impact of polyacrylamide, particularly in its usage and degradation products. Polyacrylamide is derived from acrylamide, which is recognized as a neurotoxin, raising potential health risks if not managed properly. However, when used correctly, PAM is considered safe for agricultural and industrial applications. Researchers are actively investigating methods to enhance the biodegradability of polyacrylamide, leading to environmentally friendly alternatives that minimize ecological risks.
As the demand for sustainable materials and solutions increases, the role of polyacrylamide is likely to expand further. Innovations in polymer science may pave the way for more sustainable forms of PAM that maintain efficacy while reducing environmental concerns. By balancing its beneficial applications with responsible usage and management practices, polyacrylamide can continue to be a vital material in tackling contemporary challenges across various industries.
In conclusion, polyacrylamide is a multifaceted polymer with substantial applications in agriculture, wastewater treatment, and biomedicine. Its ability to retain water, promote flocculation, and form hydrogels highlights its usefulness across diverse sectors. However, ongoing research aimed at addressing environmental concerns and enhancing biodegradability is crucial for ensuring that polyacrylamide remains a sustainable choice for the future. As technological advancements continue to shape the landscape of polymer applications, polyacrylamide stands poised to play a significant role in fostering innovation and sustainability.
-
Pbtc Scale InhibitorPBTC: A Scale Protector for Industrial Water TreatmentNewsAug.05,2025
-
Organic Phosphonate: An Efficient Defender in the Field of Scale InhibitionNewsAug.05,2025
-
Hydrolyzed Polymaleic Anhydride: Green Pioneer in Scale Inhibition FieldNewsAug.05,2025
-
PAPEMP Polyamino Polyether Methylene Phosphonic Acid For SaleNewsAug.05,2025
-
Flocculant Water Treatment: A Pioneer in Purification in the Field of Water TreatmentNewsAug.05,2025
-
Benzyl Isothiazolinone: An Efficient and Broad-Spectrum Antibacterial Protective GuardNewsAug.05,2025





