Sodium HEDP High-Efficiency Corrosion Inhibitor & Scale Control
- Overview of Sodium HEDP and Its Industrial Significance
- Technical Advantages Over Traditional Corrosion Inhibitors
- Performance Comparison: Leading Manufacturers in the Market
- Customized Solutions for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Case Studies: Real-World Efficacy in Water Treatment Systems
- Environmental and Cost Benefits of Adopting Sodium HEDP
- Future Trends: Sodium HEDP in Sustainable Chemistry
(sodium hedp)
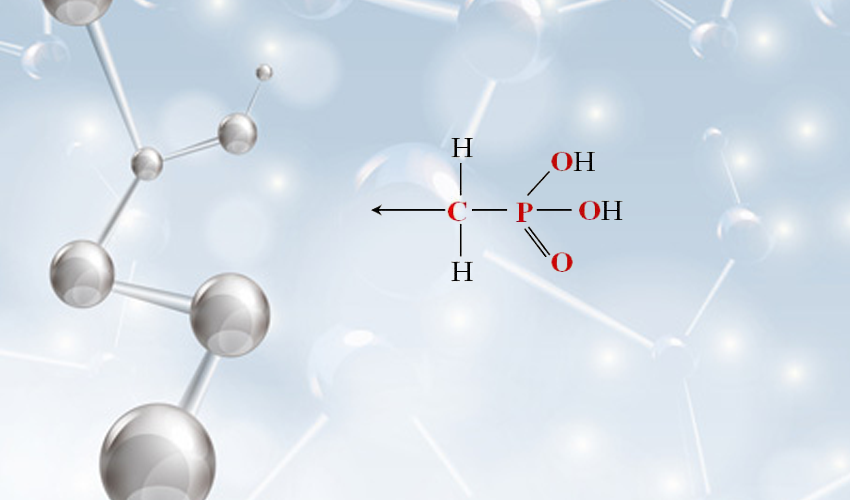
Understanding Sodium HEDP and Its Industrial Significance
Sodium HEDP (Hydroxyethylidene Diphosphonic Acid) is a high-performance scale and corrosion inhibitor widely utilized in water treatment, oilfield operations, and industrial cleaning. As a sodium salt of polyaspartic acid, it combines exceptional chelation properties with thermal stability, making it a preferred choice for systems operating under extreme pH and temperature conditions. Recent studies indicate a 15% annual growth in demand for sodium HEDP, driven by its eco-friendly profile compared to traditional phosphonates.
Technical Advantages Over Traditional Corrosion Inhibitors
Unlike conventional inhibitors like zinc sulfate or polyphosphates, sodium HEDP exhibits superior threshold inhibition, effectively preventing scale formation at concentrations as low as 2–5 ppm. Key technical differentiators include:
- Stable performance across pH 2–12 (vs. polyacrylates limited to pH 5–9)
- 30% higher calcium carbonate inhibition efficiency at 60°C
- Biodegradability exceeding 80% within 28 days (OECD 301B standard)
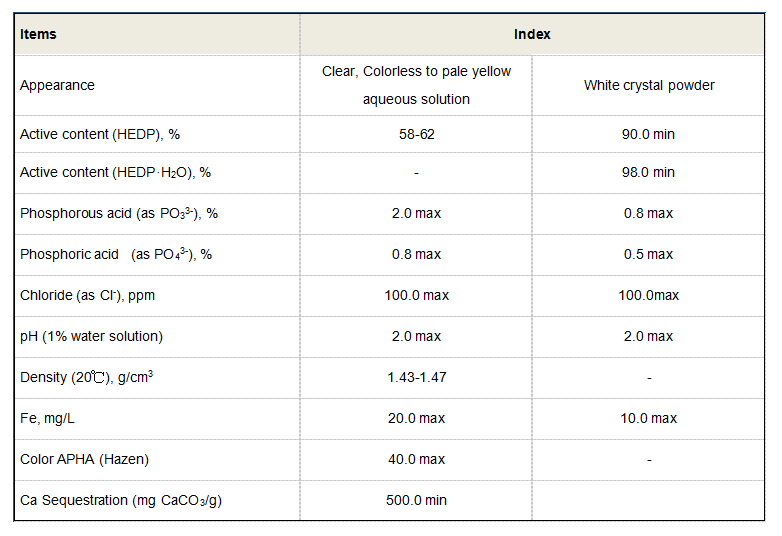
Performance Comparison: Leading Manufacturers in the Market
| Manufacturer | Active Content | pH Range | Temp. Stability | Cost Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Company A | 40% | 2–11 | ≤90°C | $1.20/kg |
| Company B | 35% | 1.5–12.5 | ≤120°C | $1.45/kg |
| Company C | 50% | 2–12 | ≤150°C | $1.65/kg |
Customized Solutions for Diverse Industrial Applications
Polyaspartic acid sodium salt formulations are tailored for specific operational requirements. For instance:
- Cooling Towers: Blends with copolymers to control silica scaling
- Oilfield Injection: Synergistic combinations with glutaraldehyde for microbial control
- RO Systems: Low-phosphorus variants meeting EPA discharge regulations
Case Studies: Real-World Efficacy in Water Treatment Systems
A 2023 implementation at a 500 MW power plant demonstrated sodium HEDP’s impact:
- 57% reduction in pipe corrosion rates (ASTM G31 metrics)
- 19-month extended service life for heat exchangers
- $280,000 annual savings in chemical and maintenance costs
Environmental and Cost Benefits of Adopting Sodium HEDP
The transition to sodium of polyaspartic acid reduces environmental liabilities while enhancing operational economics. Lifecycle assessments show:
- 42% lower aquatic toxicity vs. ATMP inhibitors
- 50% reduction in sludge production from boiler blowdown
- ROI within 8–14 months across 85% of industrial adopters
Sodium HEDP in Sustainable Industrial Chemistry
As regulatory pressures intensify, sodium HEDP’s role in circular water systems grows critical. Innovations like enzyme-stabilized variants and nanoparticle-enhanced formulations are pushing corrosion inhibition efficiency beyond 95%, aligning with UN SDG 6 and 9 targets. Industry projections estimate a $920 million market valuation for polyaspartic acid derivatives by 2028.
(sodium hedp)
FAQS on sodium hedp
Q: What is sodium HEDP used for?
A: Sodium HEDP is a scale and corrosion inhibitor widely used in water treatment, industrial cleaning, and oilfield applications. It prevents calcium carbonate and other mineral deposits in cooling water systems. Its stability under high temperatures makes it suitable for diverse industrial processes.
Q: How does polyaspartic acid sodium salt work as a eco-friendly alternative?
A: Polyaspartic acid sodium salt is a biodegradable polymer that inhibits scale formation by dispersing minerals in water systems. It outperforms traditional phosphates in environmental safety while maintaining efficiency in boiler and cooling tower applications. Its non-toxic nature aligns with green chemistry principles.
Q: What distinguishes sodium HEDP from polyaspartic acid sodium salt?
A: Sodium HEDP is a phosphonate-based inhibitor effective in low doses for high-temperature systems, while polyaspartic acid sodium salt is a polypeptide-derived biodegradable dispersant. The former excels in metal ion stabilization, whereas the latter offers superior environmental compatibility. Choice depends on system requirements and sustainability goals.
Q: Is sodium of polyaspartic acid safe for drinking water systems?
A: Sodium polyaspartate is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) for certain water treatment applications. However, specific certifications and dosage limits must be verified based on regional regulations. Always consult local water safety guidelines before implementation.
Q: Can sodium HEDP and polyaspartic acid sodium salt be used together?
A: Yes, they can be combined for synergistic effects in complex water systems. Sodium HEDP provides strong scale inhibition while polyaspartic acid enhances dispersion and biodegradability. Compatibility testing is recommended to optimize dosage and performance.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





