Alternative Water Treatment Solutions Using HEDP for Enhanced Efficacy and Efficiency
HEDP in Water Treatment An Effective Solution for Scale and Corrosion Control
Water treatment is a vital process used across various industries to ensure the quality of water for consumption, manufacturing, and other purposes. One of the critical challenges in water treatment is scale formation and corrosion, which can lead to system inefficiencies, increased maintenance costs, and even system failures. In this context, Hydroxyethylidene Diphosphonic Acid (HEDP) has emerged as a promising solution for mitigating these issues.
HEDP in Water Treatment An Effective Solution for Scale and Corrosion Control
One of the major advantages of using HEDP in water treatment is its effectiveness in preventing corrosion. Corrosion is a gradual process that occurs when metals react with their environment, leading to the deterioration of piping and equipment. HEDP, with its unique ability to form stable complexes with metal ions, acts as a corrosion inhibitor. By binding with metals such as iron and copper in the water, HEDP reduces their reactivity, thereby protecting surfaces from deterioration.
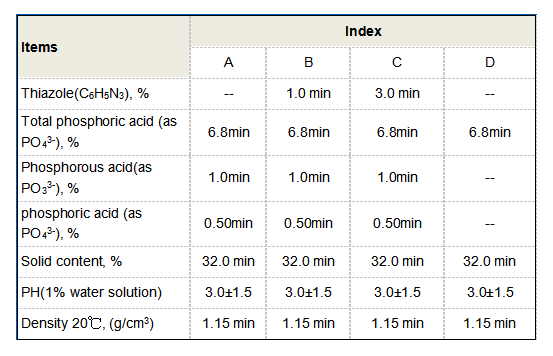
hedp water treatment
HEDP is also favored for its low toxicity and environmental impact, making it suitable for applications in various industries, including municipal water treatment, power generation, and chemical processing. Its biodegradable nature means that it breaks down in the environment without leaving harmful residues, aligning with the increasing demand for sustainable water treatment solutions.
In practical applications, HEDP can be used in conjunction with other water treatment chemicals to enhance overall performance. For instance, when combined with biocides and other scale inhibitors, it provides a comprehensive approach to managing water quality. This synergistic effect can lead to improved operational efficiency and reduced treatment costs, offering a compelling case for its use in diverse applications.
Furthermore, HEDP is easy to handle and integrate into existing water treatment systems. It is compatible with a wide range of formulations, allowing for flexibility in application methods. This adaptability has contributed to its growing popularity in both industrial and municipal settings.
In conclusion, HEDP represents a versatile and effective solution for addressing common water treatment challenges, particularly scale and corrosion control. Its ability to chelate metal ions, combined with its environmental safety profile, makes it an attractive option for industries looking to enhance their water treatment processes. As the demand for efficient and sustainable water management practices continues to rise, the role of HEDP in water treatment will likely expand, providing essential benefits to both users and the environment.
-
lk-319-special-scale-and-corrosion-inhibitor-for-steel-plants-advanced-solutions-for-industrial-water-systemsNewsAug.22,2025
-
flocculant-water-treatment-essential-chemical-solutions-for-purification-processesNewsAug.22,2025
-
isothiazolinones-versatile-microbial-control-agents-for-industrial-and-consumer-applicationsNewsAug.22,2025
-
scale-inhibitor-key-solutions-for-water-system-scale-preventionNewsAug.22,2025
-
organophosphonates-versatile-scale-inhibitors-for-industrial-water-systemsNewsAug.22,2025
-
scale-and-corrosion-inhibitor-essential-chemical-solutions-for-water-system-maintenanceNewsAug.22,2025





