hydroxyphosphonoacetic acid
Hydroxyphosphonoacetic Acid An Overview
Hydroxyphosphonoacetic acid (HPAA) is a compound of significant interest in various fields, including chemistry, pharmaceuticals, and agriculture. As a derivative of phosphonic acids, it contains both hydroxyl and phosphonic functional groups, contributing to its unique properties and versatility. This article explores the structure, functions, and applications of hydroxyphosphonoacetic acid, emphasizing its importance in contemporary science.
Structure and Properties
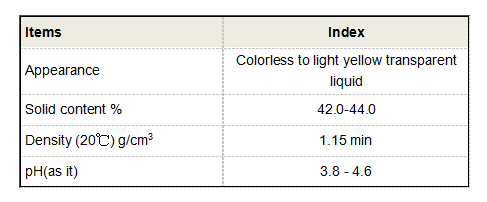
Chemically, hydroxyphosphonoacetic acid is represented by the formula C2H7O5P. The molecule consists of a phosphonic acid group (-PO3H2) attached to an acetic acid moiety (-CH2COOH), along with an additional hydroxyl group (-OH). This structural configuration grants HPAA distinct acidity, solubility characteristics, and reactivity patterns, which make it suitable for various applications.
One of the notable properties of HPAA is its ability to act as a chelating agent. The presence of both the hydroxyl group and the phosphonate group allows it to bind effectively to metal ions. This chelating ability is advantageous in certain industrial processes, helping to prevent metal ion-related interference during chemical reactions. Additionally, its solubility in water expands its usability in formulations, making it a candidate for agricultural pesticides and soil conditioning agents.
Applications in Agriculture
The agricultural sector stands out as one of the primary fields benefiting from hydroxyphosphonoacetic acid. HPAA is commonly used as an active ingredient in fertilizers and biostimulants. Due to its phosphonate structure, it can significantly enhance the availability of essential nutrients for plants, particularly phosphorus, which is known to improve root development and overall plant health.
Researchers have demonstrated that hydroxyphosphonoacetic acid can promote plant growth by influencing microbial activity in the soil. It acts as a bioavailable source of phosphorus, aiding in the solubilization of soil phosphates and enhancing plant absorption. Furthermore, HPAA contributes to improved resistance against certain plant pathogens, thanks to its antimicrobial properties.
Additionally, the ability of HPAA to chelate metal ions allows it to improve the uptake of micronutrients in plants. This characteristic is particularly beneficial in soils that are deficient in essential trace elements, thereby promoting healthier crop yields and improving food security.
hydroxyphosphonoacetic acid
Pharmaceutical Relevance
Beyond agriculture, hydroxyphosphonoacetic acid holds promise in the pharmaceutical industry. Its structural attributes enable interactions with biological systems, making it a candidate for drug development. Specifically, HPAA has been investigated for potential applications in treating diseases that involve dysregulated phosphate metabolism, such as osteoporosis and certain cancers.
Recent studies have explored the pharmacological effects of hydroxyphosphonoacetic acid, revealing its potential to inhibit specific enzymes involved in phosphate metabolism. By modulating these pathways, HPAA could become a therapeutic agent capable of restoring balance in phosphate-related disorders. Furthermore, ongoing research aims to understand its mechanism of action and optimize its efficacy in clinical applications.
Environmental Considerations
As with many chemical compounds, the environmental impacts of hydroxyphosphonoacetic acid have garnered attention. Its use in agriculture necessitates careful management to prevent runoff and contamination of water systems. The persistence and bioaccumulation potential of phosphonates are considerations that researchers, regulators, and farmers must address.
Innovative approaches to application methods, such as precision agriculture techniques, can mitigate these environmental concerns while maximizing the benefits of HPAA. This highlights the need for sustainable practices in both agricultural and industrial settings to ensure the responsible use of chemical compounds.
Conclusion
Hydroxyphosphonoacetic acid is a multifaceted compound with significant applications in agriculture and pharmaceuticals. Its unique chemical structure imparts valuable properties such as chelation and solubility, contributing to nutrient accessibility and plant health. Ongoing research may uncover new therapeutic uses and optimize its application in sustainable practices. As we advance our understanding of hydroxyphosphonoacetic acid, its role in meeting global agricultural and health challenges continues to expand, making it a subject worthy of further study and innovation.
-
Pbtc Scale InhibitorPBTC: A Scale Protector for Industrial Water TreatmentNewsAug.05,2025
-
Organic Phosphonate: An Efficient Defender in the Field of Scale InhibitionNewsAug.05,2025
-
Hydrolyzed Polymaleic Anhydride: Green Pioneer in Scale Inhibition FieldNewsAug.05,2025
-
PAPEMP Polyamino Polyether Methylene Phosphonic Acid For SaleNewsAug.05,2025
-
Flocculant Water Treatment: A Pioneer in Purification in the Field of Water TreatmentNewsAug.05,2025
-
Benzyl Isothiazolinone: An Efficient and Broad-Spectrum Antibacterial Protective GuardNewsAug.05,2025





