poly aluminium chloride in wastewater treatment
The Role of Poly Aluminium Chloride in Wastewater Treatment
In recent years, the increasing demand for clean water has led to the exploration of various methods for effective wastewater treatment. Among the numerous coagulants available, Poly Aluminium Chloride (PAC) has gained significant attention for its efficacy and versatility in treating wastewater. This inorganic polymer coagulant is widely used in municipal and industrial wastewater treatment processes due to its superior flocculation properties and better sedimentation characteristics compared to traditional coagulants like alum.
Poly Aluminium Chloride is a synthetic polymer made by neutralizing aluminium hydroxide with hydrochloric acid. Its unique structure consists of multiple aluminium ions, which provides it with strong coagulative properties. When introduced into wastewater, PAC works by destabilizing the colloidal particles present in the water, allowing them to agglomerate into larger flocs that can be easily removed from the liquid phase.
One of the significant advantages of using PAC in wastewater treatment is its high efficiency in removing suspended solids, turbidity, and inorganic impurities. Studies indicate that PAC can achieve a greater reduction in turbidity levels than traditional aluminium-based coagulants, making it particularly effective in treating surface water and industrial effluents. The formation of larger and denser flocs not only facilitates easier removal but also reduces the volume of sludge produced during the treatment process.
Additionally, PAC operates effectively across a wide range of pH values, providing flexibility in different treatment scenarios. Unlike traditional coagulants that require strict pH control, PAC can function well in acidic to slightly alkaline conditions. This attribute is crucial in wastewater treatment, where pH can fluctuate due to varying industrial processes or environmental changes.
poly aluminium chloride in wastewater treatment
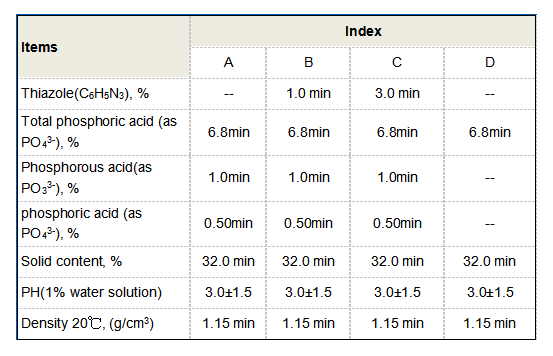
Another noteworthy benefit of PAC is its low dosage requirement compared to other coagulants. Because of its high charge density, only a small amount of PAC is needed to achieve the desired coagulation effect. This leads to cost savings not only in terms of coagulant costs but also in the reduction of sludge handling and disposal fees. Furthermore, the lower quantity of sludge generated is an essential consideration in today's environmentally conscious world, as reducing waste aligns with sustainable development goals.
In addition to these advantages, PAC’s use in wastewater treatment is also allied with its environmental safety. Unlike some chemical coagulants that can introduce harmful residues into the water system, PAC is seen as a safer alternative that minimizes the risk of toxicity to aquatic life when properly managed. Its biodegradability further enhances its profile as an environmentally friendly option for water treatment facilities.
Despite these benefits, the application of PAC does come with challenges. The effectiveness of PAC can be influenced by the characteristics of the wastewater being treated, such as the presence of natural organic matter, heavy metals, or other contaminants. Therefore, it is vital for wastewater treatment facilities to conduct thorough testing and optimization of dosages based on specific wastewater characteristics to achieve optimal performance.
In summary, Poly Aluminium Chloride emerges as a powerful coagulant in the realm of wastewater treatment, offering superior performance, cost-effectiveness, and environmental safety. Its ability to efficiently remove impurities while producing less sludge makes it a favored choice among water treatment professionals. As the global focus on water quality intensifies, the role of PAC in wastewater treatment will likely continue to grow, making it an essential component in efforts to safeguard valuable water resources for future generations. Continuous research and optimization will further enhance its application, ensuring cleaner water and a healthier environment.
-
LK-319 Special Scale And Corrosion Inhibitor For Steel Plants: Advanced Solutions for Industrial Water SystemsNewsAug.22,2025
-
Flocculant Water Treatment: Essential Chemical Solutions for Purification ProcessesNewsAug.22,2025
-
Isothiazolinones: Versatile Microbial Control Agents for Industrial and Consumer ApplicationsNewsAug.22,2025
-
Scale Inhibitor: Key Solutions for Water System Scale PreventionNewsAug.22,2025
-
Organophosphonates: Versatile Scale Inhibitors for Industrial Water SystemsNewsAug.22,2025
-
Scale and Corrosion Inhibitor: Essential Chemical Solutions for Water System MaintenanceNewsAug.22,2025





