diethylene triamine penta methylene phosphonic acid
Diethylene Triamine Penta Methylene Phosphonic Acid An Overview
Diethylene Triamine Penta Methylene Phosphonic Acid (DTPMPA) is a highly versatile chelating agent that is widely used in various applications across multiple industries. Chemical compounds such as DTPMPA play crucial roles in managing water quality and enhancing the efficacy of certain processes due to their unique properties. Understanding its structure, applications, and benefits can shed light on why DTPMPA is a significant compound in both industrial and environmental contexts.
Chemical Structure and Properties
DTPMPA belongs to the class of phosphonic acids, which are characterized by the presence of phosphonic acid functional groups. The molecular formula for DTPMPA is C10H30N3O10P5, and it can be depicted as a compound that contains five phosphonic acid groups attached to a diethylene triamine backbone. This distinctive structure imparts the chelating properties of the molecule, allowing it to bind effectively with metal ions present in various solutions.
One of the notable features of DTPMPA is its ability to form stable complexes with a wide range of metal ions including calcium, magnesium, and iron. This is particularly advantageous in water treatment processes where hardness ions can precipitate and cause scaling in pipes and machinery. The stability of the complexes formed by DTPMPA reduces the risk of unwanted deposits, thereby maintaining the efficiency of systems involved in water use.
Applications in Industry
DTPMPA is primarily employed in water treatment formulations, where it acts as an anti-scaling and corrosion inhibitor. In cooling water systems, for instance, it can prevent scale formation, which is crucial for the efficient operation of industrial processes. The presence of scales can impede heat exchange and result in increased energy consumption, making DTPMPA a valuable addition to formulation strategies aimed at enhancing energy efficiency.
diethylene triamine penta methylene phosphonic acid
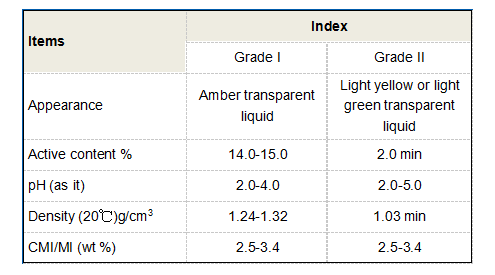
Additionally, DTPMPA is utilized in the formulation of detergents and cleaning agents. Its chelating ability allows it to bind metal ions that could interfere with the cleaning process; thus, it enhances the overall effectiveness of the detergent. This property is especially useful in areas with hard water, where high metal ion concentrations can reduce the efficacy of cleaning agents.
Moreover, DTPMPA finds applications in agriculture, particularly in formulations of fertilizers and pesticides. By chelating essential micronutrients, it improves their bioavailability, allowing for better nutrient uptake by plants. This can lead to enhanced crop yields and better overall health of the plants.
Environmental Implications
The environmental implications of using DTPMPA are also significant. Its ability to treat water efficiently means that less harmful byproducts are released into natural water bodies. Additionally, by preventing the buildup of scale and corrosion, DTPMPA contributes to the longevity of equipment and systems, reducing the frequency of replacements and the waste generated from disposed equipment.
However, like any chemical, it is vital to handle DTPMPA with care to mitigate any potential negative effects on human health and the environment. Most studies indicate that DTPMPA poses low toxicity when used as intended, making it safer compared to other alternatives in many applications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Diethylene Triamine Penta Methylene Phosphonic Acid is a powerful and multifunctional compound that has secured a vital role in various industries, particularly in water treatment, cleaning agents, and agriculture. Its unique chemical properties make it an effective chelating agent, capable of addressing challenges associated with metal ions in solutions. As industries aim for greater efficiency and sustainability, the role of compounds like DTPMPA will undoubtedly become more prominent in driving innovation and environmental stewardship.
-
Pbtc Scale InhibitorPBTC: A Scale Protector for Industrial Water TreatmentNewsAug.05,2025
-
Organic Phosphonate: An Efficient Defender in the Field of Scale InhibitionNewsAug.05,2025
-
Hydrolyzed Polymaleic Anhydride: Green Pioneer in Scale Inhibition FieldNewsAug.05,2025
-
PAPEMP Polyamino Polyether Methylene Phosphonic Acid For SaleNewsAug.05,2025
-
Flocculant Water Treatment: A Pioneer in Purification in the Field of Water TreatmentNewsAug.05,2025
-
Benzyl Isothiazolinone: An Efficient and Broad-Spectrum Antibacterial Protective GuardNewsAug.05,2025





