isothiazolinones
Understanding Isothiazolinones Their Uses, Safety, and Regulatory Challenges
Isothiazolinones are a class of synthetic biocides widely used as preservatives in various consumer products, including cosmetics, personal care items, paints, and industrial applications. The unique antimicrobial properties of isothiazolinones make them effective against a broad spectrum of bacteria and fungi, ensuring product longevity and safety. This article delves into the uses, safety concerns, regulatory landscape, and emerging alternatives to isothiazolinones.
Chemical Structure and Properties
Isothiazolinones are derived from isothiazole, a five-membered heterocyclic compound. The most common members of this group include methylisothiazolinone (MIT) and chloromethylisothiazolinone (CMIT). These compounds operate by disrupting cellular processes in microorganisms, leading to their death. Their effectiveness at low concentrations makes them valuable in formulations where preserving efficacy is crucial without compromising product integrity.
Applications
Isothiazolinones are primarily used in
1. Personal Care Products These compounds are found in shampoos, conditioners, lotions, and creams. They help prevent microbial growth that could lead to product spoilage, ensuring a safer experience for consumers.
2. Household Products Cleaning agents, detergents, and other household formulations often incorporate isothiazolinones to extend shelf life and enhance performance against mold and bacteria.
3. Industrial Applications In industries such as paper and textile, these biocides are used to prevent microbial contamination in production processes. Their use in water treatment facilities to control microbial growth is also significant.
isothiazolinones
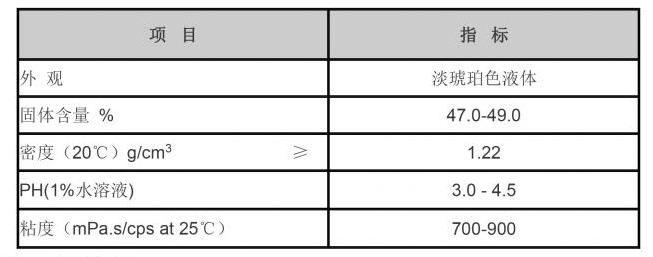
Safety Concerns
Despite their effectiveness, isothiazolinones have come under scrutiny due to safety concerns, particularly regarding skin sensitization and allergic reactions. The European Commission's Scientific Committee on Consumer Safety (SCCS) has raised warnings about the potential for these compounds to cause contact dermatitis, leading to restrictions on their concentrations in cosmetic products.
People have reported adverse reactions such as rashes and allergic responses after exposure to products containing isothiazolinones. As a result, several countries have instituted stringent regulations. In the European Union, for instance, guidelines limit the allowed concentration of MIT to 0.01% in rinse-off products and 0.0015% in leave-on products.
Regulatory Landscape
The regulatory environment for isothiazolinones varies globally. While the EU has taken significant steps to restrict their use due to safety concerns, other regions like the United States have yet to implement similar measures. However, the conversation around the safety of these compounds is growing, prompting manufacturers to reassess their formulations.
In response to the regulatory pressures and growing consumer awareness regarding the safety of personal care products, many companies are seeking alternatives to isothiazolinones. Natural preservatives, such as essential oils and plant extracts, are increasingly being explored. However, their effectiveness can vary, and they may not always be suitable for all applications or formulations.
Future Trends
The future of isothiazolinones may reflect a broader shift towards more sustainable and safer alternatives in product formulation. With increasing consumer demand for transparency and safety, manufacturers are being encouraged to innovate and find solutions that not only preserve products but also align with health and environmental considerations.
In conclusion, isothiazolinones serve a critical role in product preservation and safety across various industries. However, their associated safety concerns and regulatory challenges necessitate a careful approach to their usage. As the industry evolves, ongoing research into safer alternatives will likely shape the future landscape of biocides, ensuring efficacy without compromising consumer safety.
-
Understanding Polycarboxylic Acids: Properties, Applications, and Future PotentialNewsJul.28,2025
-
Scale Inhibitor Explained: How to Protect Your System from Limescale and Hard Water DamageNewsJul.28,2025
-
Scale and Corrosion Inhibitors: Essential Chemicals for Industrial Water System ProtectionNewsJul.28,2025
-
Polyaspartic Acid: A Biodegradable Polymer for Sustainable ChemistryNewsJul.28,2025
-
Isothiazolinones: A Versatile Antimicrobial Class with Industrial Power and Regulatory ChallengesNewsJul.28,2025
-
A Deep Dive into 2-Phosphonobutane-1,2,4-Tricarboxylic Acid (PBTC)NewsJul.28,2025





