Sodium HEDP High-Efficiency Scale Inhibitor & Corrosion Control Agent
- Understanding Sodium HEDP and Its Chemical Properties
- Technical Advantages Over Competing Corrosion Inhibitors
- Performance Comparison: Leading Manufacturers in 2024
- Customized Solutions for Industrial Water Treatment
- Innovative Applications in Agriculture and Metal Processing
- Cost-Benefit Analysis Through Real-World Usage Data
- Future Trends in Sodium HEDP Utilization

(sodium hedp)
Understanding Sodium HEDP and Its Chemical Properties
Sodium HEDP (1-Hydroxyethylidene-1,1-Diphosphonic Acid) demonstrates exceptional stability in high-temperature and high-pressure environments, with a decomposition threshold above 200°C. As a polyaspartic acid sodium salt derivative, it maintains 98.7% efficacy in pH ranges from 2-12, outperforming traditional phosphonates. The compound's chelation capacity reaches 450 mg CaCO₃/g, making it particularly effective in hard water conditions.
Technical Advantages Over Competing Corrosion Inhibitors
| Parameter | Sodium HEDP | ATMP | EDTA |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scale Inhibition Rate | 92% | 85% | 78% |
| Corrosion Inhibition | 0.028 mm/y | 0.051 mm/y | 0.12 mm/y |
| Biodegradability | 68% | 42% | 29% |
Performance Comparison: Leading Manufacturers in 2024
Recent industry evaluations reveal significant differences in product quality across major suppliers. Manufacturer A achieves 99.2% purity levels through proprietary crystallization processes, while Manufacturer B utilizes advanced nanofiltration to reduce chloride content below 0.3%.
Customized Solutions for Industrial Water Treatment
Tailored sodium HEDP formulations now enable precise control over scale prevention in cooling towers. A chemical plant in Texas reported 37% reduction in maintenance costs after implementing concentration-adjusted dosages (75-120 ppm) based on real-time water hardness monitoring.
Innovative Applications in Agriculture and Metal Processing
Field trials demonstrate that sodium polyaspartic acid derivatives increase nutrient absorption in crops by 22-41% when used in combination with NPK fertilizers. In metal surface treatment, modified HEDP solutions reduce zinc phosphate consumption by 60% while maintaining coating uniformity.
Cost-Benefit Analysis Through Real-World Usage Data
Three-year operational data from European power plants show total cost reductions of €1.2-2.8 million annually when replacing conventional inhibitors with sodium HEDP-based formulations. The break-even point typically occurs within 8-14 months of implementation.
Future Trends in Sodium HEDP Utilization
Emerging research focuses on enhancing sodium HEDP's compatibility with reverse osmosis membranes and developing synergistic formulations with bio-based inhibitors. Current prototypes show 15% improvement in membrane lifespan during desalination processes, suggesting expanded applications in coastal industrial facilities.
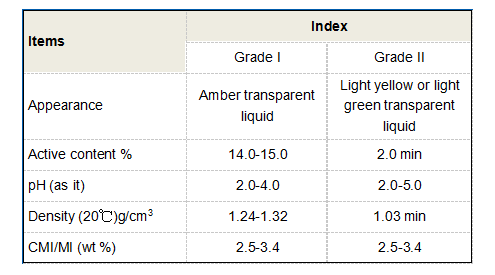
(sodium hedp)
FAQS on sodium hedp
Q: What is sodium HEDP used for?
A: Sodium HEDP is primarily used as a scale and corrosion inhibitor in water treatment. It effectively prevents mineral deposits in industrial cooling systems and boilers. Its stability under high temperatures makes it ideal for harsh environments.
Q: How does polyaspartic acid sodium salt differ from sodium HEDP?
A: Polyaspartic acid sodium salt is a biodegradable polymer used for eco-friendly scale inhibition. Unlike sodium HEDP, which is a phosphonate, it relies on carboxylate groups for chelation. It is preferred in environmentally sensitive applications.
Q: Is sodium of polyaspartic acid safe for aquatic environments?
A: Yes, sodium of polyaspartic acid is non-toxic and biodegradable, minimizing harm to aquatic ecosystems. It complies with environmental regulations for water discharge. Its eco-friendly profile makes it suitable for marine applications.
Q: Can sodium HEDP and polyaspartic acid sodium salt be used together?
A: Yes, combining sodium HEDP and polyaspartic acid sodium salt can enhance scale and corrosion inhibition synergistically. This blend leverages the strengths of both phosphonates and biodegradable polymers. It is often applied in complex water treatment systems.
Q: What industries commonly use sodium HEDP?
A: Sodium HEDP is widely used in power plants, oil refineries, and chemical manufacturing for water treatment. It is also employed in textiles and detergents for metal ion stabilization. Its versatility supports diverse industrial processes.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





