Different Types of Flocculants Used in Water Treatment Processes
Understanding Different Types of Flocculants
Flocculants play a crucial role in various industrial processes, particularly in water treatment, mining, and the food industry. These substances, which encourage the clumping together of particles to form a floc, are essential for separating solids from liquids and improving efficiency in various processes. Understanding the different types of flocculants is vital for selecting the right one for specific applications. In this article, we will delve into the primary flocculant types, their functions, and where they are typically applied.
1. Natural Flocculants
Natural flocculants are derived from natural sources, including plant or animal substances. One of the most common examples is starch, which acts as a flocculant by binding particles together in various water treatment processes. Other natural flocculants include gelatin and guar gum, both of which are used in food processing to clarify liquids and improve texture.
Natural flocculants are often preferred in applications where environmental impact is a concern. They tend to be biodegradable and non-toxic, making them suitable for treating water that will eventually be released back into the environment. However, they might be less effective in certain conditions compared to synthetic options.
Synthetic flocculants are chemical formulations designed to enhance the aggregation of particles. They are often more versatile and effective than their natural counterparts. The most common synthetic flocculants are polyacrylamide-based products, which can be tailored to different molecular weights and charge densities, thereby allowing for specific applications.
These synthetic flocculants can be anionic, cationic, or nonionic. Anionic flocculants carry a negative charge, making them effective in conditions where positively charged particles need to be aggregated. Cationic flocculants, on the other hand, possess a positive charge and are effective for negatively charged particles, commonly used in water treatment and papermaking. Nonionic flocculants, which have no charge, can be used in various settings where both anionic and cationic interactions occur.
3. Inorganic Flocculants
flocculant types
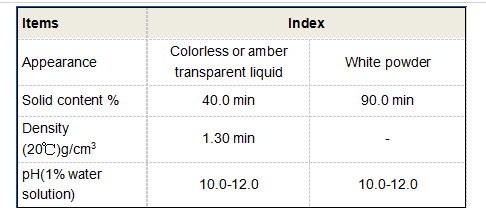
Inorganic flocculants are minerals and metal-based compounds, often utilized due to their high effectiveness and low cost. Aluminum sulfate (often referred to as alum) is one of the most commonly used inorganic flocculants, especially in drinking water treatment. Alum works by neutralizing the charge of suspended particles, causing them to clump together and settle out of suspension.
Another example is ferric chloride, which is effective for removing organic matter and is commonly used in municipal wastewater treatment plants. While inorganic flocculants are effective, they can sometimes lead to the formation of sludge by-products that require further treatment.
4. Biopolymer Flocculants
Biopolymer flocculants are a new class gaining traction due to their sustainability and efficiency. Made primarily from renewable resources such as polysaccharides or proteins, these flocculants offer biodegradable solutions without the environmental impact associated with some synthetic chemicals.
Instances of biopolymer flocculants include chitosan, derived from chitin found in crustacean shells. It has shown promising results in water treatment processes due to its natural flocculating ability and non-toxic nature. This type of flocculant is ideal for applications requiring minimal environmental disruption.
5. Application-Specific Flocculants
Different industries may require custom formulations designed for specific conditions or contaminants. For instance, in the mining industry, flocculants may be selected based on the type of ore being processed and the nature of the tailings. In the food industry, flocculants are utilized not only for clarification but also for stabilizing emulsions.
Conclusion
Choosing the right type of flocculant is essential for achieving optimal performance in various applications, from water treatment to food production. Each type—natural, synthetic, inorganic, and biopolymer—has its unique advantages and challenges. By understanding their distinct characteristics, industries can select the most appropriate flocculants to meet their specific needs while ensuring environmental compliance and efficiency.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





