flocculant vs coagulant
Understanding the Difference Flocculant vs. Coagulant
In the world of water treatment, two terms often come up flocculants and coagulants. While both play crucial roles in the clarification of water, they serve distinct purposes within the water treatment process. Understanding their differences is important for anyone involved in water treatment operations, environmental engineering, or even just curious about how clean water is produced.
Understanding the Difference Flocculant vs
. CoagulantOnce coagulation has occurred, the next step in the water treatment process is flocculation. This is where flocculants come into play. Flocculants are long-chain polymers that help bind the newly-formed clumps or flocs together, creating larger aggregates that can be easily settled or filtered out of the water. The flocculation process involves gentle mixing, which encourages these larger aggregates to form without breaking apart. Flocculants are typically used after coagulants in a treatment sequence and can significantly enhance the sedimentation rate of the flocs. Common flocculants include polyacrylamides, natural starches, and various natural gums.
flocculant vs coagulant
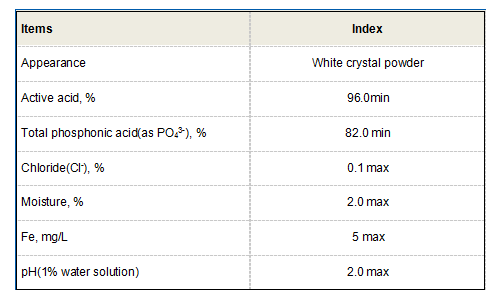
While they serve interconnected purposes in the water treatment process, flocculants and coagulants differ significantly in their composition and functionality. Coagulants tend to be inorganic or low molecular weight compounds, while flocculants are typically synthetic high molecular weight polymers. This difference in structure leads to distinct functions coagulants focus on destabilizing particles, whereas flocculants emphasize enhancing floc formation and settling.
The choice between using a coagulant or a flocculant—or even both—depends heavily on the specific characteristics of the water being treated. Factors such as turbidity levels, particle size distribution, and water chemistry all play significant roles in determining the appropriate agent to use. For instance, in turbid waters with high particulate loads, the initial application of a coagulant might be sufficient to bring particles together. However, if the resultant flocs are too small or weak, a flocculant would be necessary to ensure a robust settling process.
Moreover, environmental considerations are increasingly influencing the choice of both coagulants and flocculants. As regulations tighten and the push for eco-friendly treatments grows, many industries are exploring biodegradable and renewable alternatives to traditional synthetic chemicals.
In conclusion, both flocculants and coagulants are indispensable in the water treatment process, each contributing uniquely to the removal of impurities and the clarity of water. By understanding their respective roles, operators can optimize treatment processes, enhance performance, and comply with environmental standards. This knowledge is not only essential for professionals in the field but also for anyone interested in the intricacies of how our water systems operate. The next time you turn on your tap, you'll have a better appreciation of the processes that ensure the water is not only safe but also clean and clear.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





