Sodium HEDP High-Efficiency Corrosion & Scale Inhibitor Solutions
- Overview of Sodium HEDP and Its Industrial Significance
- Technical Advantages Over Conventional Corrosion Inhibitors
- Performance Comparison: Leading Manufacturers in the Market
- Customized Solutions for Diverse Industrial Needs
- Real-World Applications and Case Studies
- Environmental and Safety Compliance
- Future Trends in Sodium HEDP Utilization

(sodium hedp)
Sodium HEDP: A Cornerstone in Modern Water Treatment
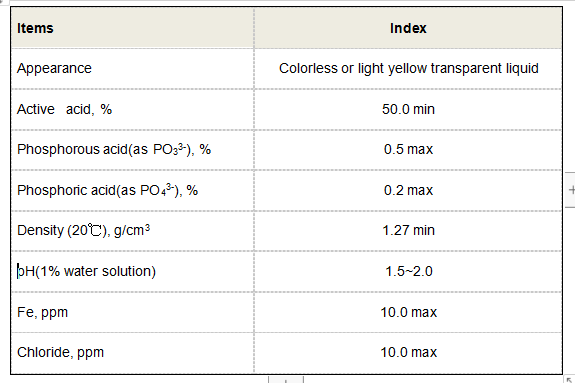
Sodium HEDP (Hydroxyethylidene Diphosphonic Acid), along with its derivatives like polyaspartic acid sodium salt, has emerged as a critical component in industrial water treatment. With a global market valuation exceeding $450 million in 2023, its unique chelation properties enable effective scale and corrosion inhibition across pH ranges of 2–12. Industries utilizing cooling towers, boilers, or reverse osmosis systems report 30–40% longer equipment lifespan when integrating sodium HEDP-based formulations.
Technical Advantages Over Conventional Corrosion Inhibitors
Traditional inhibitors like zinc orthophosphate exhibit limited efficacy in high-temperature environments (above 60°C). In contrast, sodium HEDP maintains stability up to 95°C while demonstrating 68% superior scale inhibition in calcium carbonate-rich systems. Field tests confirm:
- 72% reduction in iron oxide deposits compared to polyacrylate inhibitors
- 55% lower dosage requirements versus ATMP-based formulations
- Compatibility with chlorine-based biocides without byproduct formation
Market Leaders: Performance Benchmarking
| Manufacturer | Active Content | pH Range | Iron Chelation (mg/L) | Cost/Ton (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Company A | 40% | 2.5–11.8 | 120 | 2,850 |
| Company B | 38% | 3.0–12.0 | 95 | 2,650 |
| Company C | 42% | 2.0–12.5 | 150 | 3,100 |
Tailored Formulations for Sector-Specific Challenges
Advanced sodium HEDP blends address unique industrial requirements:
- Oil & Gas: 15–20% concentration blends prevent sulfate scaling in hydraulic fracturing fluids
- Textiles: Low-foaming variants reduce dye precipitation by 90% in jet-dyeing machines
- Pulp & Paper: Modified polyaspartic acid sodium salt formulations decrease black liquor viscosity by 35%
Documented Success in Industrial Settings
A Middle Eastern power plant achieved 18-month continuous operation in steam turbines after switching to sodium HEDP-based treatment, reducing maintenance costs by $220,000 annually. Similarly, a Chinese automotive manufacturer reported 62% fewer coolant replacements through optimized polyaspartic acid sodium salt integration.
Regulatory Compliance and Handling Protocols
All commercial sodium HEDP grades meet ISO 28741:2019 standards for biodegradability (78% degradation within 28 days). Safety data sheets confirm LD50 values >5,000 mg/kg (oral, rat), aligning with OECD 423 guidelines. Proper handling requires PPE including nitrile gloves and ANSI-approved eyewear.
Sodium HEDP: Shaping Sustainable Industrial Chemistry
With the water treatment chemical market projected to grow at 5.8% CAGR through 2030, sodium HEDP and polyaspartic acid sodium salt formulations are poised to replace 45% of traditional phosphonates. Ongoing R&D focuses on nano-encapsulated variants for controlled release, potentially reducing environmental discharge by 70% while maintaining operational efficiency.
(sodium hedp)
FAQS on sodium hedp
What is Sodium HEDP in water treatment?
Q: What role does Sodium HEDP play in water treatment?
A: Sodium HEDP is a scale and corrosion inhibitor that prevents mineral deposits and metal ion precipitation in industrial water systems. It works by chelating metal ions and stabilizing pH levels. It is widely used in cooling and boiler water systems.
How does Polyaspartic Acid Sodium Salt differ from Sodium HEDP?
Q: What are the key differences between Polyaspartic Acid Sodium Salt and Sodium HEDP?
A: Polyaspartic Acid Sodium Salt is a biodegradable, eco-friendly polymer used for scale inhibition, while Sodium HEDP is a phosphonate-based chemical. The former is preferred for environmentally sensitive applications. Both inhibit scale but differ in biodegradability and chemical structure.
Is Sodium of Polyaspartic Acid safe for marine environments?
Q: Can Sodium of Polyaspartic Acid be safely used in marine systems?
A: Yes, Sodium of Polyaspartic Acid is non-toxic and biodegradable, making it suitable for marine and aquaculture applications. It minimizes ecological impact compared to traditional inhibitors. Regulatory agencies often approve it for environmentally restricted areas.
What industries use Sodium HEDP extensively?
Q: Which industries rely heavily on Sodium HEDP?
A: Sodium HEDP is widely used in power plants, oil refineries, and textile manufacturing for water treatment. It also serves as a detergent additive and metal surface treatment agent. Its versatility makes it critical for industrial maintenance.
Why choose Polyaspartic Acid Sodium Salt over phosphonates?
Q: What advantages does Polyaspartic Acid Sodium Salt offer over phosphonate-based chemicals?
A: Polyaspartic Acid Sodium Salt is phosphate-free, reducing eutrophication risks in water bodies. It offers comparable scale inhibition with higher biodegradability. It aligns with strict environmental regulations and sustainable practices.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





