hydroxyphosphonoacetic acid
Hydroxyphosphonoacetic Acid An Overview
Hydroxyphosphonoacetic acid, often abbreviated as HPA, is an organic compound that has garnered attention in various fields, including biochemistry, agriculture, and pharmaceuticals. Characterized by its unique chemical structure, the compound features a phosphonic acid group combined with a hydroxy and carboxylic acid functional group. This dual functionality endows HPA with a diverse range of applications, thanks to its ability to interact with various biochemical pathways and environmental processes.
Structure and Properties
HPA is a member of the phosphonic acid family, which includes a phosphorus atom bonded to a hydroxyl group, a carboxyl group, and a hydrogen atom. This specific arrangement allows hydroxyphosphonoacetic acid to exhibit both acidic and chelating properties. As a chelating agent, HPA can bind to metal ions, which is particularly useful in agricultural and environmental applications where metal ion removal is desired.
The solubility of HPA in water is another advantageous property, facilitating its use in liquid formulations. Its moderate pH range makes it versatile for various biochemical reactions, enabling its effectiveness in different environmental conditions. Moreover, the presence of both hydroxyl and carboxylic acid groups contributes to its reactivity with nucleophiles, making it a compound of interest in synthetic chemistry.
Applications in Agriculture
One of the primary applications of hydroxyphosphonoacetic acid lies in the realm of agriculture. It has been investigated as a growth-promoting agent for crops, particularly in conditions where soil nutrients are limited or where soil pH is not optimal for plant growth. HPA's chelating properties allow it to mobilize essential nutrients, such as calcium, iron, and magnesium, making them more bioavailable to plants. This ability not only enhances plant growth but also leads to improved crop yields, making HPA a valuable tool for sustainable agricultural practices.
hydroxyphosphonoacetic acid
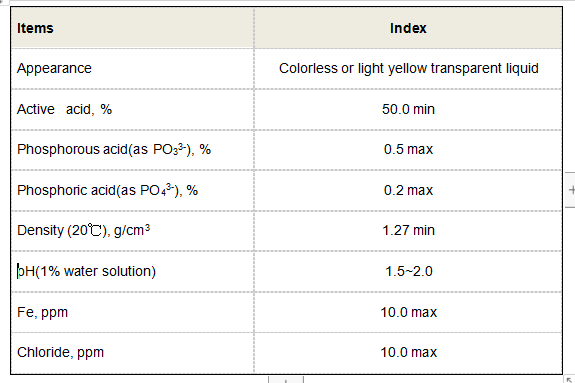
Furthermore, studies have shown that HPA can improve the efficacy of certain herbicides by promoting their absorption and effectiveness against weeds. This synergy between HPA and herbicidal agents highlights its potential in integrated pest management strategies, contributing to more efficient and ecologically sound agricultural practices.
Role in Pharmaceutical Research
In pharmaceuticals, hydroxyphosphonoacetic acid has been explored for its role in drug formulation and as a potential therapeutic agent. Its capacity to form stable complexes with metal ions can be utilized in targeted drug delivery systems, enhancing the efficacy of specific therapies, particularly those involving metal-based drugs. Additionally, research indicates that HPA may possess antioxidant properties, which could be beneficial in the development of treatments for various oxidative stress-related diseases.
Moreover, HPA’s unique structure allows for modifications that can lead to the synthesis of a wide range of derivatives, expanding its potential applications in drug discovery and development. The exploration of these derivatives could open new avenues in addressing health crises by providing innovative solutions to prevalent diseases.
Future Directions
As research on hydroxyphosphonoacetic acid continues, its multifaceted applications promise significant advancements in various fields. Further studies are necessary to fully understand its mechanisms of action, particularly in biological systems and environmental interactions. The ongoing exploration of HPA and its derivatives could lead to the development of novel agrochemicals and pharmaceuticals, fostering a more sustainable approach to agriculture and healthcare.
In conclusion, hydroxyphosphonoacetic acid is a compound with immense potential. Its unique properties and versatile applications position it as a key player in the pursuit of innovative solutions for pressing challenges in agriculture and medicine.
-
Pbtc Scale InhibitorPBTC: A Scale Protector for Industrial Water TreatmentNewsAug.05,2025
-
Organic Phosphonate: An Efficient Defender in the Field of Scale InhibitionNewsAug.05,2025
-
Hydrolyzed Polymaleic Anhydride: Green Pioneer in Scale Inhibition FieldNewsAug.05,2025
-
PAPEMP Polyamino Polyether Methylene Phosphonic Acid For SaleNewsAug.05,2025
-
Flocculant Water Treatment: A Pioneer in Purification in the Field of Water TreatmentNewsAug.05,2025
-
Benzyl Isothiazolinone: An Efficient and Broad-Spectrum Antibacterial Protective GuardNewsAug.05,2025





