Exploring the Role of Coagulants and Flocculants in Water Treatment Processes and Applications
The Role of Coagulants and Flocculants in Water Treatment
Water treatment is a crucial process that ensures access to clean and safe water for consumption and various industrial applications. Among the vital chemicals employed in this process, coagulants and flocculants play a significant role. Understanding their functions and differences is essential for optimizing water purification processes.
What are Coagulants?
Coagulants are chemical agents that help to remove suspended solids from water by promoting the aggregation of particles into larger clusters or flocs. When water is contaminated with particulate matter, such as dirt, silt, and other impurities, these small particles often carry a negative charge and repel one another, making it difficult for them to settle out of the water. Coagulants neutralize these charges, allowing the particles to stick together and form larger aggregates that can be more easily removed from the water.
Common coagulants include aluminum sulfate (alum), ferric chloride, and polyaluminum chloride. These chemicals are typically added to water in a controlled manner, after which they react with the impurities, initiating the coagulation process. The effectiveness of coagulants can depend on factors such as pH, temperature, and the specific characteristics of the water being treated.
The Role of Flocculants
While coagulants initiate the aggregation of particles, flocculants enhance this process by promoting the formation of larger, more stable flocs that can be easily removed through sedimentation or filtration. Flocculants are usually long-chain polymers that help to bridge the gaps between smaller flocs, creating a loosely bound structure that is more efficient in separating from the water.
Flocculants can be categorized into different types, including anionic, cationic, and nonionic, depending on their charge properties. The choice of flocculant can significantly impact the efficacy of the water treatment process, as different flocculants are suited for varying conditions and types of contaminants.
coagulant flocculant
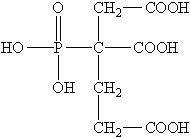
The Synergistic Effect of Coagulants and Flocculants
Using coagulants and flocculants in tandem can dramatically improve the efficiency of the water treatment process. Coagulants first reduce the repulsive forces between charged particles, facilitating the initial aggregation. Following this, flocculants further encourage the growth of these aggregates, leading to larger and more easily removable flocs. This synergistic approach not only enhances the clarification and settling of solids but can also reduce the overall dosage of chemicals needed, lowering operational costs and minimizing environmental impact.
Considerations in Water Treatment
When selecting coagulants and flocculants, several factors must be taken into account, such as the nature of the water source, the type and concentration of contaminants, and the desired quality of the treated water. Laboratories often perform jar tests to determine the optimal types and doses of these chemicals for specific water compositions.
Moreover, environmental considerations are increasingly influencing the choice of coagulants and flocculants. Many municipalities are seeking more environmentally friendly options, which has led to the development of bio-based and biodegradable alternatives.
Conclusion
Coagulants and flocculants are indispensable components of modern water treatment processes, working together to enhance the removal of impurities from water. As technology advances and the demand for clean water continues to grow, the importance of these chemicals in delivering safe, clean drinking water cannot be overstated. Understanding their roles and optimizing their use will be critical to addressing water quality challenges around the globe.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





