Exploring the Versatile Applications and Properties of Polyacrylamide in Various Industries and Research Fields
The Role of Polyacrylamide in Various Industries
Polyacrylamide (PAM) is a synthetic polymer that has garnered significant attention across various industrial sectors due to its versatile properties and applications. As a water-soluble polymer, polyacrylamide is composed of acrylamide monomers, which can be polymerized to form a wide range of derivatives, subsequently expanding its utility in differing contexts. This article explores the importance of polyacrylamide, its applications, advantages, and emerging trends in utilizing this polymer.
1
. Applications of PolyacrylamidePolyacrylamide's primary feature is its ability to form a gel-like structure when hydrated, making it extremely useful in numerous applications. One of the most notable uses is in water treatment, where PAM serves as a flocculant. In this setting, it aids in the aggregation of suspended particles and contaminants in wastewater, facilitating their removal. This application is pivotal in municipal wastewater treatment plants, as well as in industrial settings where large volumes of water are processed.
Another prominent application of polyacrylamide is in the agriculture sector, especially in soil stabilization and erosion control. When applied to the soil, PAM enhances moisture retention, reduces runoff, and minimizes erosion, leading to improved agricultural productivity. Through the formation of stable soil aggregates, polyacrylamide helps create a conducive environment for plant growth, which is crucial in regions facing severe water scarcity.
In the oil and gas industry, polyacrylamide is employed in enhanced oil recovery (EOR) processes. By improving the viscosity of water used in injection processes, PAM enhances oil displacement efficiency, thus optimizing extraction rates. As energy demands continue to rise, the role of polyacrylamide in boosting oil recovery cannot be underestimated.
Moreover, polyacrylamide finds applications in the cosmetics and personal care industry. It is often used as a thickening agent and stabilizer in various formulations, providing desirable textures and improved product consistency.
2. Advantages of Polyacrylamide
polyacrylamide p3
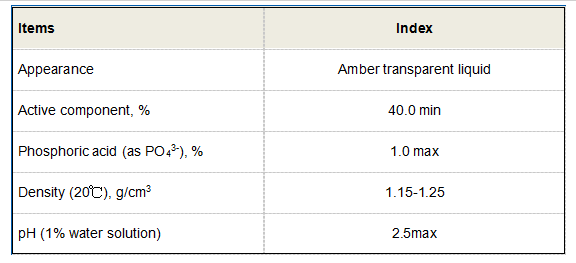
The popularity of polyacrylamide can be attributed to its numerous advantages. First and foremost, PAM is highly effective even at low concentrations. This efficiency translates to cost savings for industries that utilize it since smaller amounts can yield significant benefits.
Additionally, polyacrylamide is non-toxic and biodegradable, which addresses growing environmental concerns associated with synthetic chemicals. Its ability to enhance the performance of various processes while being environmentally friendly makes it an attractive choice for companies aiming to adhere to sustainability principles.
Moreover, the versatility of polyacrylamide allows it to be chemically modified, thus tailoring its properties to meet specific needs. This customization further expands its applicability across different sectors, making PAM a crucial component in many formulations and processes.
3. Emerging Trends and Future Perspectives
As research and technology continue to evolve, the applications of polyacrylamide are expected to expand. Innovations in polymer chemistry may lead to the development of new PAM formulations that enhance performance or reduce environmental impact. For instance, there is ongoing research into bio-based polyacrylamide alternatives that could offer similar benefits with lower ecological footprints.
Furthermore, advancements in nanotechnology might pave the way for polyacrylamide's application in drug delivery systems, where its gel-forming capabilities can be harnessed to create controlled release systems for pharmaceuticals.
In conclusion, polyacrylamide stands as a multifaceted polymer with diverse applications that cut across water treatment, agriculture, energy recovery, and cosmetics. Its advantages of efficiency, non-toxicity, and versatility solidify its position as an essential compound in numerous industries. As technological advancements continue to unfold, the future of polyacrylamide appears promising, with potential innovations poised to enhance its utility and sustainability.
-
Understanding Polycarboxylic Acids: Properties, Applications, and Future PotentialNewsJul.28,2025
-
Scale Inhibitor Explained: How to Protect Your System from Limescale and Hard Water DamageNewsJul.28,2025
-
Scale and Corrosion Inhibitors: Essential Chemicals for Industrial Water System ProtectionNewsJul.28,2025
-
Polyaspartic Acid: A Biodegradable Polymer for Sustainable ChemistryNewsJul.28,2025
-
Isothiazolinones: A Versatile Antimicrobial Class with Industrial Power and Regulatory ChallengesNewsJul.28,2025
-
A Deep Dive into 2-Phosphonobutane-1,2,4-Tricarboxylic Acid (PBTC)NewsJul.28,2025





