anionic polyacrylamide price
Understanding the Price Dynamics of Anionic Polyacrylamide
Anionic polyacrylamide (APAM) is a popular water-soluble polymer that finds extensive applications across various industries, including agriculture, mining, petroleum, and wastewater treatment. Its effectiveness as a flocculating agent and a soil conditioner has made it a staple in these sectors. However, the price of anionic polyacrylamide can fluctuate significantly based on a multitude of factors, impacting its market dynamics.
Understanding the Price Dynamics of Anionic Polyacrylamide
Market demand plays a critical role in determining APAM prices. Industries such as agriculture and wastewater treatment have seen a growing demand for effective and environmentally friendly solutions, which has driven the need for polyacrylamide compounds. For instance, in agriculture, APAM is used for soil erosion control and improving water retention in soil, which has become increasingly important in the face of climate change. As demand in these sectors increases, manufacturers may raise prices to balance supply and demand.
anionic polyacrylamide price
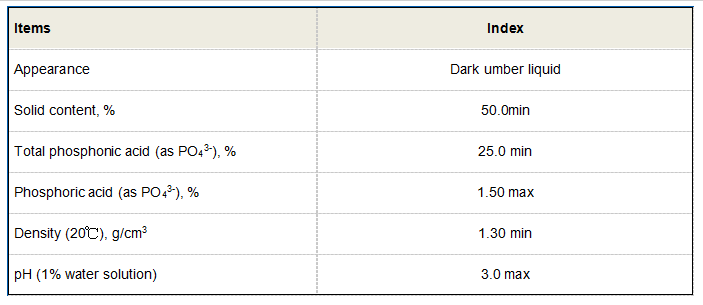
Moreover, the geographical location of production facilities can impact the cost of anionic polyacrylamide. Regions with lower labor and operational costs may offer APAM at more competitive prices compared to regions where manufacturing costs are higher. This can lead to a variance in pricing across different markets, affecting international trade and competition among suppliers.
Furthermore, regulations and environmental considerations are increasingly shaping the price of anionic polyacrylamide. As governments impose stricter regulations on chemical substances, manufacturers may need to invest in compliance measures, which can lead to increased production costs. If the production process is made more sustainable, it may also drive up costs initially before stabilizing as processes become more efficient.
Another consideration is the technological advancements in the production of polyacrylamide. Innovations that improve yield and reduce waste not only enhance product quality but can also lead to cost reductions over time. If new production technologies lower the cost of APAM manufacturing, prices in the market may decrease, benefiting end users.
In conclusion, the price of anionic polyacrylamide is subject to a myriad of factors ranging from raw material costs and market demand to geographical influences and regulatory frameworks. Stakeholders in industries that rely on APAM must stay informed about these dynamics to navigate pricing fluctuations effectively. As demand continues to grow, especially within environmentally conscious applications, understanding these price factors will be essential for strategic procurement and market positioning.
-
Understanding Polycarboxylic Acids: Properties, Applications, and Future PotentialNewsJul.28,2025
-
Scale Inhibitor Explained: How to Protect Your System from Limescale and Hard Water DamageNewsJul.28,2025
-
Scale and Corrosion Inhibitors: Essential Chemicals for Industrial Water System ProtectionNewsJul.28,2025
-
Polyaspartic Acid: A Biodegradable Polymer for Sustainable ChemistryNewsJul.28,2025
-
Isothiazolinones: A Versatile Antimicrobial Class with Industrial Power and Regulatory ChallengesNewsJul.28,2025
-
A Deep Dive into 2-Phosphonobutane-1,2,4-Tricarboxylic Acid (PBTC)NewsJul.28,2025





