Applications and Benefits of Anionic Polyacrylamide in Water Treatment and Agriculture
Anionic Polyacrylamide Properties, Applications, and Environmental Considerations
Anionic polyacrylamide (APAM) is a synthetic polymer that has gained significant attention in various industries due to its unique properties and versatility. Created through the polymerization of acrylamide with anionic groups, this substance exhibits characteristics that make it valuable in applications ranging from water treatment to agricultural enhancement.
Properties of Anionic Polyacrylamide
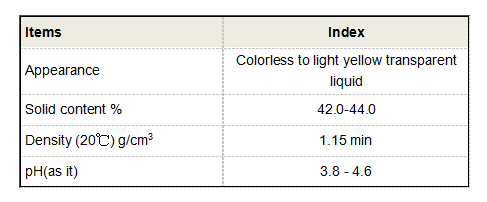
APAM is known for its high molecular weight and anionic nature, which results in a strong negative charge. This charge facilitates its ability to interact with positively charged particles, promoting flocculation and coagulation processes. The structure of APAM allows it to form a gel-like consistency in aqueous solutions. Its solubility in water and compatibility with various ionic conditions make it particularly effective in diverse environments.
The viscosity of APAM solutions can vary depending on the concentration and molecular weight of the polymer used. Higher molecular weights generally lead to increased viscosity, which is beneficial for applications requiring thickening or stabilization. Additionally, APAM is stable under a wide range of pH conditions, which contributes to its effectiveness in different industrial processes.
Applications of Anionic Polyacrylamide
The applications of APAM are extensive and varied
1. Water Treatment One of the primary uses of anionic polyacrylamide is in water treatment processes. It plays a crucial role in the coagulation and flocculation of suspended solids, helping to clarify water in municipal and industrial applications. By binding to impurities and forming larger aggregates, APAM aids in the sedimentation and removal of contaminants from water.
2. Agriculture In agriculture, APAM is utilized to improve soil and water conservation. It helps reduce soil erosion by increasing soil structure stability and water retention. Furthermore, it enhances the uptake of water and nutrients by plants, promoting better crop yields, especially in arid regions.
anionic polyacrylamide
3. Oil and Gas Industry The oil and gas sector employs APAM in drilling fluids, where it serves as a viscosity modifier and helps stabilize the mud systems. It aids in the removal of cuttings and minimizes fluid loss, improving overall efficiency during drilling operations.
4. Mining In the mining industry, anionic polyacrylamide is used for ore processing and wastewater management. It assists in the separation of valuable minerals from waste materials and ensures that effluents meet environmental regulations before discharge.
5. Paper and Pulp Industry APAM is utilized to enhance the drainage, retention, and formation processes in the production of paper. Its use leads to improved fiber retention and product quality while reducing water consumption.
Environmental Considerations
Despite its wide range of applications, the use of anionic polyacrylamide raises some environmental concerns. The primary ingredient, acrylamide, is recognized as a hazardous substance. While APAM itself is considered relatively safe, the degradation of unreacted acrylamide in the environment can pose risks to aquatic life and human health.
To mitigate these concerns, it is crucial to adhere to proper usage guidelines and treatment processes. APAM should be used in controlled environments where its application can be monitored to ensure minimal environmental impact. Additionally, ongoing research into biodegradable alternatives or modified versions of polyacrylamide aims to reduce the ecological footprint associated with its use.
Conclusion
Anionic polyacrylamide is an invaluable polymer with diverse applications across various industries, particularly in water treatment, agriculture, and mining. Its unique properties enable it to interact effectively with different materials, making it a powerful tool for enhancing operational efficiency. However, awareness of the environmental implications associated with its use is essential. Through responsible usage and ongoing research, the benefits of APAM can be harnessed while minimizing its impact on ecosystems, prompting a sustainable approach to its application. As industries continue to seek efficient solutions for environmental challenges, anionic polyacrylamide will likely remain a critical component in advancing these efforts.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





