cas 40372-66-5
The compound with the CAS number 204372-66-5 is known as N-Acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC), which is a widely studied chemical used in various applications, most notably in medicine and supplementation. NAC is a derivative of the amino acid cysteine and has garnered attention due to its antioxidant properties and its role as a precursor to glutathione, one of the body's most important antioxidants.
.
Beyond its use in acute medical emergencies, NAC has been investigated for its potential benefits in a range of chronic conditions. Studies suggest that NAC may help alleviate symptoms in diseases characterized by oxidative stress, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), cystic fibrosis, and even mental health disorders like depression and bipolar disorder. Its ability to modulate glutathione levels and exert anti-inflammatory effects may contribute to improved lung function and a reduction in inflammation in these conditions.
cas 40372-66-5
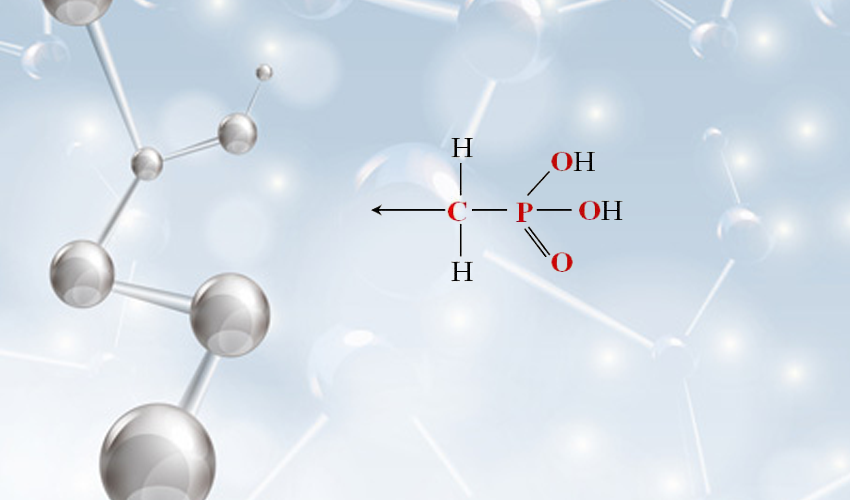
Furthermore, NAC is marketed as a dietary supplement, appealing to a broad audience interested in health and wellness. It is often touted for its purported benefits in enhancing mental clarity, supporting immune function, and promoting detoxification. Some athletes also use NAC to potentially improve performance and recovery, owing to its antioxidant properties.
Although NAC is generally regarded as safe, potential side effects can occur, including gastrointestinal issues or allergic reactions in sensitive individuals. Therefore, it is essential for users to consult with healthcare professionals before beginning any new supplement regimen.
As research continues to expand our understanding of NAC, its implications in various fields are becoming increasingly significant. From emergency medicine to chronic disease management and antioxidant support, N-Acetyl-L-cysteine exhibits a versatility that underscores its importance in both clinical and wellness contexts. Overall, its multifaceted roles highlight the intricate connections between nutrition, supplementation, and health, paving the way for further exploration of its potential benefits and applications in modern medicine.
-
Pbtc Scale InhibitorPBTC: A Scale Protector for Industrial Water TreatmentNewsAug.05,2025
-
Organic Phosphonate: An Efficient Defender in the Field of Scale InhibitionNewsAug.05,2025
-
Hydrolyzed Polymaleic Anhydride: Green Pioneer in Scale Inhibition FieldNewsAug.05,2025
-
PAPEMP Polyamino Polyether Methylene Phosphonic Acid For SaleNewsAug.05,2025
-
Flocculant Water Treatment: A Pioneer in Purification in the Field of Water TreatmentNewsAug.05,2025
-
Benzyl Isothiazolinone: An Efficient and Broad-Spectrum Antibacterial Protective GuardNewsAug.05,2025





