cationic polyacrylamide
Cationic Polyacrylamide An Overview
Cationic polyacrylamide (CPAM) is a type of water-soluble polymer that has gained significant attention in various industrial applications. This synthetic polymer is derived from acrylamide and has cationic (positively charged) functional groups, which impart unique properties making it versatile for numerous applications. This article delves into the characteristics, production methods, and a variety of applications of cationic polyacrylamide.
Characteristics of Cationic Polyacrylamide
Cationic polyacrylamide is known for its high molecular weight and excellent solubility in water. The cationic groups within the polymer chains enhance its effectiveness in binding and interacting with negatively charged particles, which is a crucial feature in many applications. The degree of cationic charge can be controlled during the polymerization process, allowing customization of the polymer for specific purposes.
These polymers typically exhibit high viscosity and film-forming ability, which contribute to their effectiveness as flocculants and coagulants. They are also stable under various pH levels, making them suitable for diverse environmental conditions. Additionally, CPAM's biodegradability makes it an attractive option for industries looking to minimize their environmental impact.
Production Methods
The production of cationic polyacrylamide involves the polymerization of acrylamide using various techniques, including solution polymerization, emulsion polymerization, and bulk polymerization. The introduction of quaternary ammonium salts or other cationic monomers during polymerization is crucial for obtaining the desired cationic properties. Control over the molecular weight and cationic charge density is essential to tailor the properties of the final product for specific applications.
cationic polyacrylamide
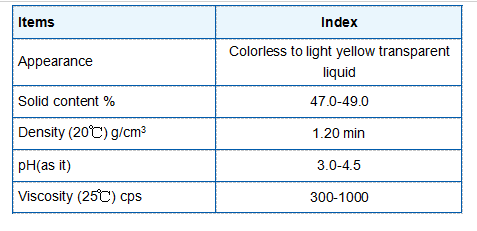
The polymerization process requires careful management of reaction conditions, including temperature, pH, and the use of initiators to ensure the quality and performance of the CPAM produced. Safety measures are also paramount due to the potential toxicity of acrylamide monomers.
Applications of Cationic Polyacrylamide
Cationic polyacrylamide has a myriad of applications across various industries due to its unique properties. One of the most significant uses is in wastewater treatment. CPAM acts as a flocculant, helping to aggregate suspended particles in water, thereby facilitating their removal. This property is particularly valuable in municipal wastewater treatment plants, as well as in industrial processes where pollutants must be effectively managed.
In the paper industry, CPAM is utilized as a retention agent and a drainage aid. Its ability to enhance fiber retention and improve the drainage process contributes to higher quality paper products and increased production efficiency. Furthermore, cationic polyacrylamide is employed in the oil and gas sector, where it aids in enhanced oil recovery and in drilling mud formulations.
Beyond industrial applications, cationic polyacrylamide is also used in cosmetics and personal care products. Its thickening and stabilizing properties enhance the texture and performance of lotions, creams, and gels.
Conclusion
Cationic polyacrylamide is a multifunctional polymer with a wide range of applications spanning various industries. Its unique chemical characteristics, coupled with its efficient performance in water treatment, paper manufacturing, and other fields, highlight its importance in modern industrial processes. As sustainability becomes increasingly important, the biodegradable nature of CPAM positions it as a favorable option for companies seeking environmentally responsible materials. With ongoing research and development, the potential applications and formulations of cationic polyacrylamide are likely to expand, further enhancing its role in innovation across diverse sectors.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





