cationic polyacrylamide uses
Cationic polyacrylamide (CPAM) is a versatile and important polymer widely used across various industries due to its unique properties. This water-soluble polymer is derived from acrylamide, possessing a positive charge that enhances its capability to interact with negatively charged particles in solution. As a result, CPAM finds applications in several fields, including water treatment, papermaking, mineral processing, and soil improvement.
One of the most prominent uses of cationic polyacrylamide is in water treatment processes. Municipalities and industries utilize CPAM for coagulation and flocculation, essential steps in purifying drinking water and treating wastewater. When CPAM is added to contaminated water, it effectively bonds with suspended particles and impurities. This bonding leads to the formation of larger aggregates or flocs, which can be easily removed from the water during filtration or sedimentation processes. The use of CPAM not only increases the efficiency of water treatment systems but also contributes to producing cleaner and safer water for consumption.
.
Another significant application of cationic polyacrylamide is in mineral processing. The mineral industry often deals with slurries containing finely divided solid particles suspended in water. CPAM aids in the separation of valuable minerals from gangue materials through flocculation, which improves the efficiency of processes like flotation and sedimentation. The ability of CPAM to enhance the settling rates of particles results in better recovery rates of minerals, making it a valuable additive in this sector.
cationic polyacrylamide uses
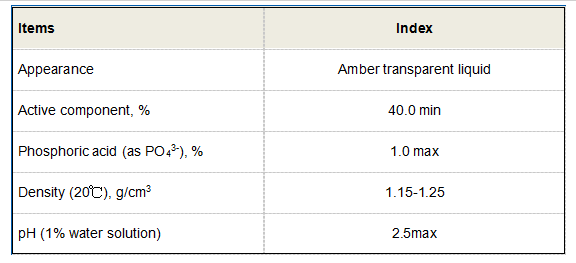
Furthermore, cationic polyacrylamide is utilized in agriculture for soil stabilization and enhancement of water retention capacity. When applied to soil, CPAM helps to bind soil particles together, reducing erosion and improving soil structure. This is particularly beneficial in areas prone to erosion or where soil degradation is a concern. Additionally, the use of CPAM in agricultural settings can increase the soil's water retention capabilities, leading to better crop yields and efficient water usage.
The effectiveness of cationic polyacrylamide, however, raises concerns regarding its environmental impact. The potential toxicity of acrylamide, a monomer used in its production, poses health risks if not managed correctly. Therefore, manufacturers and users of CPAM must adhere to stringent regulations regarding its use and disposal. Ongoing research aims to develop safer, biodegradable alternatives that retain the beneficial properties of traditional CPAM while minimizing environmental concerns.
In conclusion, cationic polyacrylamide is an essential polymer with various critical applications that enhance efficiency across multiple industries. From water treatment and papermaking to mineral processing and agriculture, CPAM plays a vital role in improving processes and outcomes. Its ability to effectively interact with particles in various contexts not only makes it a valuable tool but also highlights the need for careful management of its environmental impact. As industries continue to innovate, cationic polyacrylamide will undoubtedly remain a key player in advancing technologies for a more sustainable future.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





