cationic polyacrylamide uses
Cationic Polyacrylamide Uses and Applications
Cationic polyacrylamide (CPAM) is a versatile and widely used polymer known for its ability to enhance the efficiency of various industrial processes. As a water-soluble polymer, it is characterized by its positively charged functional groups, which allow it to interact readily with negatively charged materials in different environments. Due to its unique properties, CPAM finds a multitude of applications across diverse industries, including water treatment, paper manufacturing, mining, and agriculture.
Water Treatment
One of the most significant applications of cationic polyacrylamide is in water treatment. Due to its flocculating properties, CPAM is used to coagulate and precipitate suspended particles in wastewater, leading to clearer and cleaner water. In municipal and industrial wastewater treatment plants, CPAM helps in the removal of impurities, including oils, heavy metals, and organic matter. The positively charged nature of CPAM allows it to bind with negatively charged contaminants, forming larger flocs that can be easily removed during the filtration process. Its effectiveness in treating low to medium turbidity waters makes it a staple in both primary and secondary wastewater treatment processes.
Paper Manufacturing
In the paper industry, cationic polyacrylamide serves multiple functions. It is primarily used as a retention aid, which improves the retention of fibers and fillers during the papermaking process. This retention is crucial as it enhances paper quality and reduces material loss, ultimately leading to cost savings. Additionally, CPAM contributes to improved drainage rates, which speeds up the production process. Moreover, the polymer's bonding ability between fibers improves the strength and quality of the finished paper product. As such, CPAM is extensively used in the production of various types of paper, including newsprint, printing paper, and packaging materials.
cationic polyacrylamide uses
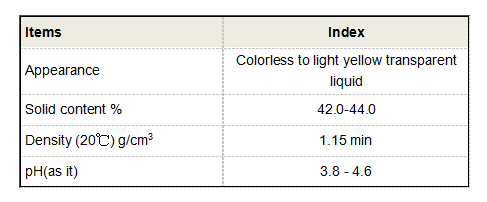
Mining Industry
In the mining industry, cationic polyacrylamide is employed primarily as a flocculant in mineral processing. Its ability to facilitate the separation of minerals from water and slurries is invaluable in the extraction and processing of metals and minerals. When added to slurries, CPAM enhances the settling rates of solids, thereby improving the overall efficiency of the mining operation. Additionally, it helps in tailings management by promoting the settling of suspended solids, minimizing waste and environmental impact. This application is crucial in ensuring sustainable mining practices.
Agriculture
Cationic polyacrylamide also plays a vital role in agriculture, particularly in soil conditioning and erosion control. When applied to soil, CPAM can improve water retention, which is beneficial in arid and semi-arid regions. This water retention capability not only enhances the soil's capacity to support plant growth but also reduces the need for frequent irrigation, promoting water conservation. Moreover, CPAM can stabilize soil structures, preventing erosion caused by wind and water. This application is particularly important in maintaining the integrity of agricultural lands, especially in regions prone to heavy rainfall or strong winds.
Conclusion
In summary, cationic polyacrylamide is a multifunctional polymer with a wide array of applications in various industries. Its effectiveness as a flocculant in water treatment, retention aid in paper manufacturing, enhancer in mineral processing, and soil conditioner in agriculture highlights its significance in promoting efficiency and sustainability. As industries continue to seek innovative solutions to improve processes and minimize environmental impacts, the demand for cationic polyacrylamide is likely to increase. Its role in facilitating cleaner production and resource conservation ensures that CPAM will remain an important component across sectors for years to come.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





