Exploring the Applications and Benefits of Diethylenetriamine Pentamine in Various Industries
Understanding Diethylenetriamine Penta
Diethylenetriamine penta (DTPA) is a chemical compound that plays a significant role in various industrial and scientific applications. This chelating agent is commonly used for its ability to form stable complexes with metal ions, enhancing its efficacy in multiple processes ranging from medicine to water treatment. This article will delve into the nature of DTPA, its uses, and its significance in various fields.
Chemical Structure and Properties
DTPA, often represented by its chemical formula C10H19N3O10, is a polyaminocarboxylic acid. Its structure comprises five carboxylic acid groups that enable it to bind effectively with metal ions. The chelation process involves the formation of a stable ring-like structure between the metal ion and the DTPA molecules, which can significantly reduce the reactivity of the metal within a solution. This property is pivotal in managing and mitigating the impacts of heavy metals, making DTPA an invaluable compound in the industry.
Applications in Medicine
One of the primary applications of DTPA is in the field of medicine, particularly in the diagnosis and treatment of heavy metal poisoning. DTPA is used as a chelating agent in therapies designed to remove excess metals such as lead, mercury, and uranium from the body. When administered, DTPA binds to these toxic metals, facilitating their excretion through urine. This detoxification process is crucial for individuals who have been exposed to harmful levels of heavy metals, thus preventing long-term health complications.
Additionally, DTPA is utilized in nuclear medicine for radiopharmaceuticals. For example, DTPA can bind to certain radioisotopes, allowing for imaging and diagnostic procedures that are less invasive and more efficient. These applications further highlight the versatility and importance of DTPA in patient care.
diethylenetriamine penta
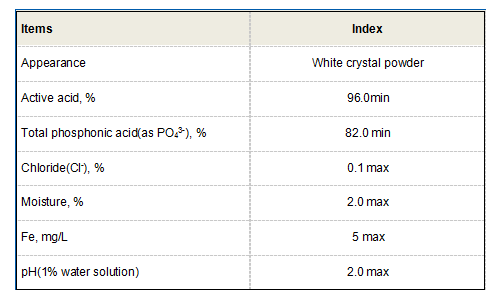
Role in Water Treatment
Beyond the medical field, DTPA is also significant in environmental applications, particularly in water treatment. Heavy metal contamination in water sources is a pressing issue globally, and DTPA is employed to sequester these metals, thereby mitigating their effects on aquatic life and human health. By binding with heavy metals, DTPA ensures that they remain in a non-toxic and soluble form, facilitating easier removal from contaminated water supplies.
Moreover, in agricultural practices, DTPA is used in fertilizers to enhance the bioavailability of micronutrients like iron. This helps in improving soil health and promoting plant growth, ensuring that crops receive adequate nutrition even in soils with low micronutrient levels.
Significance in Research
In addition to its practical applications, DTPA serves as a useful tool in scientific research. It aids in studying metal ion chemistry and the interactions between metals and biological systems. Researchers often utilize DTPA in analytical chemistry to assess metal concentrations, understand their behavior in various environments, and devise strategies for environmental remediation.
Conclusion
Diethylenetriamine penta is a multifaceted compound that bridges the gap between various disciplines, including medicine, environmental science, and agricultural chemistry. Its ability to effectively chelate metal ions not only facilitates medical treatments for heavy metal poisoning but also plays an essential role in maintaining environmental safety. The continued research and development of DTPA and its derivatives may pave the way for novel applications and enhanced methods for managing metal toxicity in both humans and ecosystems. As we advance in our understanding of such compounds, the potential for innovation remains vast, underscoring the importance of DTPA in both current and future applications.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





