flocculant chemicals for water treatment
Flocculant Chemicals for Water Treatment
Water treatment is an essential process that ensures clean and safe water for public consumption, agricultural use, and industrial applications. Among the various methods employed in water treatment processes, flocculation plays a pivotal role. It involves the aggregation of suspended particles in water, leading to their removal through sedimentation and filtration. The effectiveness of this process largely depends on the use of flocculant chemicals.
Flocculants are chemical agents that enhance the aggregation of fine particles into larger flocs, which can be easily separated from water. These chemicals can be classified into two main categories organic and inorganic flocculants. Organic flocculants are typically derived from natural materials such as polysaccharides or synthetic polymers, while inorganic flocculants often include metal salts like aluminum sulfate and ferric chloride.
The mechanism by which flocculants operate involves charge neutralization and bridging. When added to water, flocculants neutralize the electrical charges that stabilize fine particles, allowing them to come together and form larger clumps. In addition to charge neutralization, flocculants may also function as bridging agents, connecting separate particles to form a network of flocs that can settle more easily.
flocculant chemicals for water treatment
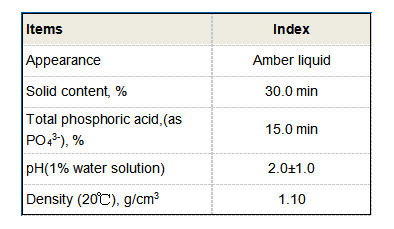
The choice of flocculant is critical and depends on various factors, including the type of contaminants present in the water, the desired quality of treated water, and the overall treatment process. For example, polyacrylamide is a commonly used organic flocculant in industrial applications due to its high efficiency in binding particles. However, its use must be carefully managed to avoid any adverse environmental impacts.
Flocculants significantly improve the efficiency of sedimentation and filtration processes in water treatment plants. By enhancing the removal of suspended solids, pollutants, and turbidity, flocculants help achieve water quality standards set by health and environmental agencies. This is vital to safeguarding public health and protecting ecosystems.
Moreover, the use of flocculants can lead to cost savings in water treatment operations. By facilitating the removal of contaminants, they can reduce the need for extensive additional treatments or equipment, thus lowering operational expenses. Additionally, effective flocculation can minimize the volume of sludge generated during treatment, making waste management simpler and more environmentally friendly.
In conclusion, flocculant chemicals are indispensable in the water treatment process. Their ability to enhance the aggregation and removal of contaminants ensures the production of clean water for various uses. As research continues to advance, the development of more effective and environmentally friendly flocculants is expected, further improving water treatment methodologies for a sustainable future.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





