Flocculants Utilized for Effective Water Treatment Processes and Applications
Flocculants Used in Water Treatment An Overview
Water treatment is a vital process that ensures the availability of clean and safe drinking water. Among the various methods employed to purify water, the use of flocculants plays a crucial role. Flocculants are substances that promote the agglomeration of particles in water, leading to the formation of larger aggregates, or flocs, that can be easily removed from the water supply. This article aims to provide an overview of the flocculants used in water treatment, their mechanisms, benefits, and types.
The Mechanism of Flocculation
Flocculation processes are primarily based on the principles of particle aggregation. In natural water bodies, various suspended particles such as organic matter, silt, clay, and microorganisms can cause turbidity, making the water unsuitable for consumption. Flocculants work by neutralizing the electrostatic charges on these particles, facilitating their aggregation. Once flocs are formed, they can be removed through sedimentation or filtration, thus clarifying the water.
The process typically involves adding a flocculant to the water, which can be followed by gentle mixing to ensure even distribution. This mixing helps the flocculant interact with suspended particles, leading to their aggregation and subsequent removal. The effectiveness of flocculants depends on various factors, including water chemistry, temperature, and the presence of other contaminants.
Types of Flocculants
Flocculants can be broadly categorized into two main groups inorganic flocculants and organic flocculants.
1. Inorganic Flocculants These are commonly used in municipal water treatment facilities due to their effectiveness and cost-efficiency. One of the most widely utilized inorganic flocculants is aluminum sulfate (alum). When added to water, alum hydrolyzes to form aluminum hydroxide, which acts as a coagulant, binding with suspended particles to form flocs. Another common inorganic flocculant is ferric chloride, which operates similarly to alum but can be more effective in certain conditions, especially in highly turbid waters.
2. Organic Flocculants These synthetic polymers are increasingly gaining popularity due to their high efficiency at low doses and their ability to function in a wide range of conditions. Polyacrylamides are one of the most frequently used organic flocculants. They can be tailored to different molecular weights and charge densities, allowing them to remove a broad spectrum of contaminants effectively. Other examples include cationic, anionic, and nonionic polymers, each of which has specific applications depending on the water chemistry.
flocculants used in water treatment
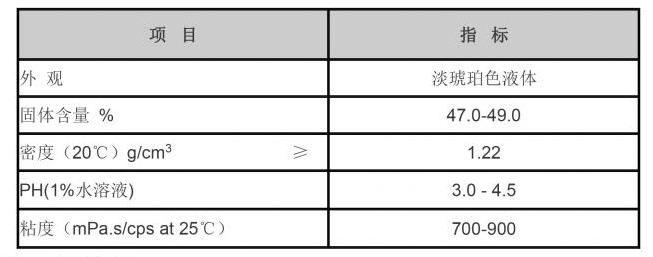
Benefits of Using Flocculants
The use of flocculants in water treatment provides several benefits
- Improved Water Quality Flocculants enhance the removal of suspended solids, organic matter, and microbial contaminants, leading to better water quality and safety for human consumption.
- Reduced Chemical Consumption By increasing the efficiency of the coagulation process, flocculants can reduce the amount of other chemicals required in water treatment, leading to cost savings and lower environmental impact.
- Versatility Different flocculants can be used to address specific water quality issues, making them applicable for a variety of water conditions, from municipal wastewaters to industrial effluents.
- Environmentally Friendly Options With advancements in technology, many newer flocculants are designed to be environmentally safe, biodegradable, and less toxic, contributing to sustainable water treatment practices.
Conclusion
Flocculants play a pivotal role in modern water treatment processes, significantly improving the quality and safety of drinking water. As water resources become increasingly strained due to pollution and population growth, the importance of effective treatment methods like flocculation cannot be overstated. With continuing research and development, the future of flocculants looks promising, providing increasingly efficient and environmentally friendly solutions for water treatment challenges around the world. Effective flocculation not only enhances water quality but also promotes public health and environmental sustainability.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





