Feb . 13, 2025 11:19
Back to list
flocculant vs coagulant
In the realm of water treatment, understanding the interplay between flocculants and coagulants is crucial for achieving optimal results. These chemical agents, though often lumped together, play distinct and complementary roles in water purification processes across various industries. Let's delve into the nuances of these substances, highlighting their experiences, expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness in practical applications.
Moreover, the mining industry benefits substantially from the use of coagulants and flocculants. During mineral processing, fine solid particles are often suspended in the liquid extract. Using reagents like anionic or non-ionic flocculants significantly enhances the recovery rate of valuable minerals while minimizing water usage and waste generation. The success of any treatment process depends on the careful selection and dosing of these chemicals. Variables such as temperature, pH, and the nature of the particles involved can significantly influence the choice between different coagulant and flocculant types. Advanced technologies, including jar testing and real-time monitoring systems, enable operators to fine-tune their processes for maximum efficiency. In environmentally sensitive applications, there's growing advocacy for the use of biodegradable or less toxic alternatives. This shift is driven by increasing regulatory pressures and a heightened public consciousness around environmental sustainability. Thus, integrating greener options without compromising on performance is a burgeoning area of research and development within the industry. The distinction and complementary roles of flocculants and coagulants underscore the importance of expertise in their application. As these chemicals are instrumental in ensuring the safety and quality of water, they also reinforce the trustworthiness and reputational integrity of industries that rely on them. They not only meet regulatory standards but also enhance operational efficiency and environmental stewardship. Through measured application, informed by thorough research and technological advancements, industries can witness enhanced clarity, compliance, and cost-effectiveness in their water treatment processes. As we advance, achieving balance in the use of flocculants and coagulants will remain pivotal, driving innovation and ecological responsibility across sectors.
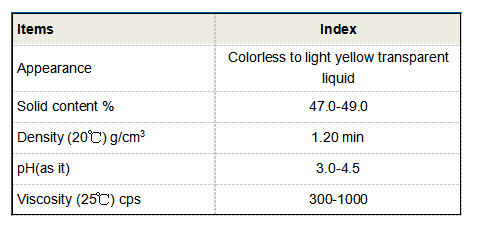

Moreover, the mining industry benefits substantially from the use of coagulants and flocculants. During mineral processing, fine solid particles are often suspended in the liquid extract. Using reagents like anionic or non-ionic flocculants significantly enhances the recovery rate of valuable minerals while minimizing water usage and waste generation. The success of any treatment process depends on the careful selection and dosing of these chemicals. Variables such as temperature, pH, and the nature of the particles involved can significantly influence the choice between different coagulant and flocculant types. Advanced technologies, including jar testing and real-time monitoring systems, enable operators to fine-tune their processes for maximum efficiency. In environmentally sensitive applications, there's growing advocacy for the use of biodegradable or less toxic alternatives. This shift is driven by increasing regulatory pressures and a heightened public consciousness around environmental sustainability. Thus, integrating greener options without compromising on performance is a burgeoning area of research and development within the industry. The distinction and complementary roles of flocculants and coagulants underscore the importance of expertise in their application. As these chemicals are instrumental in ensuring the safety and quality of water, they also reinforce the trustworthiness and reputational integrity of industries that rely on them. They not only meet regulatory standards but also enhance operational efficiency and environmental stewardship. Through measured application, informed by thorough research and technological advancements, industries can witness enhanced clarity, compliance, and cost-effectiveness in their water treatment processes. As we advance, achieving balance in the use of flocculants and coagulants will remain pivotal, driving innovation and ecological responsibility across sectors.
Share
Latest news
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





