formation atmp
Formation of the ATMP An Overview
The term ATMP, which stands for Advanced Therapy Medicinal Products, refers to a new and innovative class of medicinal products that are aimed at advanced therapeutic applications. This category encompasses three main types of therapies gene therapies, somatic-cell therapies, and tissue-engineered products. The formation of ATMP represents a significant paradigm shift in the field of medicine, particularly for the treatment of chronic diseases, genetic disorders, and injuries that traditional therapeutic approaches have struggled to address effectively.
The emergence of ATMPs has transformed the landscape of healthcare by enabling targeted, personalized treatment options that can address the root causes of diseases rather than merely alleviating symptoms. This is particularly noteworthy in the context of genetic disorders, where conventional therapies often fall short. Gene therapy, for instance, holds promise by introducing correct copies of genes into a patient’s cells, potentially curing genetic conditions that were previously deemed incurable.
Formation of the ATMP An Overview
The formation of ATMPs is also driven by advancements in scientific research and technology. Innovations in fields such as biotechnology, genetic engineering, and material science have paved the way for the creation of these advanced products. For example, technologies like CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing have revolutionized our ability to manipulate genetic material with unprecedented precision. Such innovations enable researchers and clinicians to develop targeted therapies tailored to individual genetic make-ups, effectively personalizing treatment.
formation atmp
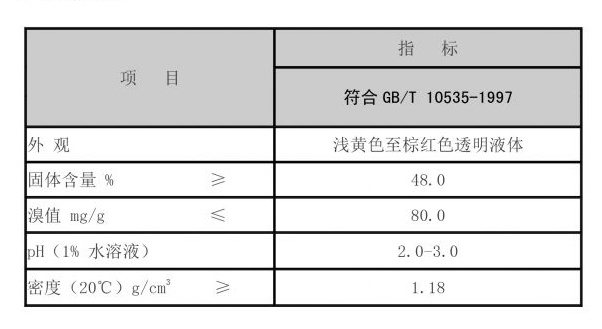
Moreover, the collaborative efforts between academic institutions, biotechnology companies, and healthcare providers have significantly contributed to the formation of ATMPs. Research consortia and public-private partnerships have facilitated knowledge exchange, resource sharing, and technological advancements. These collaborations have accelerated the progressive translation of scientific discoveries into viable therapeutic options for patients, underscoring the importance of a synergistic approach within the biosciences community.
Despite their promise, the journey towards broad implementation of ATMPs is not without challenges. Manufacturing processes for these products are complex and require specialized facilities and technologies. Additionally, regulatory scrutiny around long-term safety data and potential ethical considerations further complicate the landscape. As such, stakeholders within the healthcare ecosystem—including researchers, regulators, and manufacturers—must remain committed to navigating these challenges collaboratively.
Ultimately, the formation of Advanced Therapy Medicinal Products represents a monumental step forward in our quest for effective healthcare solutions. By harnessing the power of biomedicine and innovative technologies, ATMPs have the potential to redefine therapeutic possibilities and improve the quality of life for countless patients around the globe. As research continues and our understanding of the human genome and cellular mechanisms deepens, the future of ATMPs looks promising, filled with opportunities for breakthroughs that could change the face of medicine as we know it.
In conclusion, ATMPs are not only a testament to human ingenuity but also a beacon of hope for patients suffering from conditions that previously lacked effective treatments. Their ongoing development and integration into routine clinical practice will require continued support and investment from all sectors of society, ensuring that the benefits of this revolutionary class of therapies reach everyone who needs them.
-
Pbtc Scale InhibitorPBTC: A Scale Protector for Industrial Water TreatmentNewsAug.05,2025
-
Organic Phosphonate: An Efficient Defender in the Field of Scale InhibitionNewsAug.05,2025
-
Hydrolyzed Polymaleic Anhydride: Green Pioneer in Scale Inhibition FieldNewsAug.05,2025
-
PAPEMP Polyamino Polyether Methylene Phosphonic Acid For SaleNewsAug.05,2025
-
Flocculant Water Treatment: A Pioneer in Purification in the Field of Water TreatmentNewsAug.05,2025
-
Benzyl Isothiazolinone: An Efficient and Broad-Spectrum Antibacterial Protective GuardNewsAug.05,2025





