Jun . 12, 2024 14:40
Back to list
HEDP price remains stable for now.
The Dynamics of HEDP Price An Economic Perspective
The Hydroxy Ethylidene Diphosphonic Acid (HEDP), a crucial chemical compound widely used in water treatment, industrial cleaning, and metal processing, has been a subject of keen interest in the global market due to its fluctuating price trends. HEDP, with its unique ability to inhibit scale formation and corrosion, plays a pivotal role in numerous industries, making its pricing dynamics a significant factor for stakeholders.
Over the past few years, the HEDP market has witnessed a roller-coaster ride in terms of pricing. The HEDP% price is influenced by a multitude of factors, including raw material availability, production capacity, demand-supply dynamics, and global economic conditions.
Firstly, the cost of raw materials, primarily ethylene oxide and phosphorous acid, directly impacts the HEDP price. Any fluctuations in their prices, driven by factors like weather conditions, geopolitical tensions, or changes in government policies, can lead to a shift in the HEDP% price. For instance, a sudden surge in crude oil prices, from which ethylene oxide is derived, could push up the HEDP production cost and subsequently its market price.
Secondly, the capacity utilization of manufacturers significantly affects the HEDP% price. If there's an overcapacity, producers might lower prices to maintain sales volume, while undercapacity could lead to price hikes due to scarcity. Technological advancements that improve production efficiency can also influence the price, as they may reduce manufacturing costs Technological advancements that improve production efficiency can also influence the price, as they may reduce manufacturing costs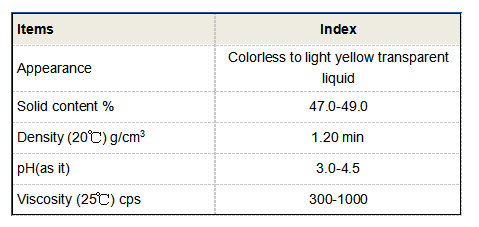 Technological advancements that improve production efficiency can also influence the price, as they may reduce manufacturing costs Technological advancements that improve production efficiency can also influence the price, as they may reduce manufacturing costs
Technological advancements that improve production efficiency can also influence the price, as they may reduce manufacturing costs Technological advancements that improve production efficiency can also influence the price, as they may reduce manufacturing costs hedp price.
Thirdly, the global demand for HEDP, particularly from the rapidly growing water treatment and power generation sectors, plays a vital role. Regions with high industrialization and urbanization rates, such as Asia Pacific, tend to drive the demand, impacting the HEDP% price. Conversely, during economic downturns, reduced industrial activities could lead to a decrease in demand, softening the market price.
Moreover, international trade policies and tariffs can also sway the HEDP% price. Tariffs on imported HEDP can increase the overall cost for consumers, whereas free trade agreements can facilitate more affordable access, driving down prices.
In conclusion, the HEDP% price is a complex interplay of various economic, technological, and geopolitical factors. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for manufacturers, distributors, and end-users to make informed decisions in this competitive market landscape. As the world continues to grapple with challenges like water scarcity and industrial growth, the significance of HEDP and its pricing trends will only become more pronounced.
hedp price.
Thirdly, the global demand for HEDP, particularly from the rapidly growing water treatment and power generation sectors, plays a vital role. Regions with high industrialization and urbanization rates, such as Asia Pacific, tend to drive the demand, impacting the HEDP% price. Conversely, during economic downturns, reduced industrial activities could lead to a decrease in demand, softening the market price.
Moreover, international trade policies and tariffs can also sway the HEDP% price. Tariffs on imported HEDP can increase the overall cost for consumers, whereas free trade agreements can facilitate more affordable access, driving down prices.
In conclusion, the HEDP% price is a complex interplay of various economic, technological, and geopolitical factors. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for manufacturers, distributors, and end-users to make informed decisions in this competitive market landscape. As the world continues to grapple with challenges like water scarcity and industrial growth, the significance of HEDP and its pricing trends will only become more pronounced.
 Technological advancements that improve production efficiency can also influence the price, as they may reduce manufacturing costs Technological advancements that improve production efficiency can also influence the price, as they may reduce manufacturing costs
Technological advancements that improve production efficiency can also influence the price, as they may reduce manufacturing costs Technological advancements that improve production efficiency can also influence the price, as they may reduce manufacturing costs hedp price.
Thirdly, the global demand for HEDP, particularly from the rapidly growing water treatment and power generation sectors, plays a vital role. Regions with high industrialization and urbanization rates, such as Asia Pacific, tend to drive the demand, impacting the HEDP% price. Conversely, during economic downturns, reduced industrial activities could lead to a decrease in demand, softening the market price.
Moreover, international trade policies and tariffs can also sway the HEDP% price. Tariffs on imported HEDP can increase the overall cost for consumers, whereas free trade agreements can facilitate more affordable access, driving down prices.
In conclusion, the HEDP% price is a complex interplay of various economic, technological, and geopolitical factors. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for manufacturers, distributors, and end-users to make informed decisions in this competitive market landscape. As the world continues to grapple with challenges like water scarcity and industrial growth, the significance of HEDP and its pricing trends will only become more pronounced.
hedp price.
Thirdly, the global demand for HEDP, particularly from the rapidly growing water treatment and power generation sectors, plays a vital role. Regions with high industrialization and urbanization rates, such as Asia Pacific, tend to drive the demand, impacting the HEDP% price. Conversely, during economic downturns, reduced industrial activities could lead to a decrease in demand, softening the market price.
Moreover, international trade policies and tariffs can also sway the HEDP% price. Tariffs on imported HEDP can increase the overall cost for consumers, whereas free trade agreements can facilitate more affordable access, driving down prices.
In conclusion, the HEDP% price is a complex interplay of various economic, technological, and geopolitical factors. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for manufacturers, distributors, and end-users to make informed decisions in this competitive market landscape. As the world continues to grapple with challenges like water scarcity and industrial growth, the significance of HEDP and its pricing trends will only become more pronounced. Share
Latest news
-
Understanding Polycarboxylic Acids: Properties, Applications, and Future PotentialNewsJul.28,2025
-
Scale Inhibitor Explained: How to Protect Your System from Limescale and Hard Water DamageNewsJul.28,2025
-
Scale and Corrosion Inhibitors: Essential Chemicals for Industrial Water System ProtectionNewsJul.28,2025
-
Polyaspartic Acid: A Biodegradable Polymer for Sustainable ChemistryNewsJul.28,2025
-
Isothiazolinones: A Versatile Antimicrobial Class with Industrial Power and Regulatory ChallengesNewsJul.28,2025
-
A Deep Dive into 2-Phosphonobutane-1,2,4-Tricarboxylic Acid (PBTC)NewsJul.28,2025





