hydrolyzed polyacrylamide
Hydrolyzed Polyacrylamide An Overview of its Applications and Benefits
Hydrolyzed polyacrylamide (HPAM) is a derivative of polyacrylamide, a polymer formed by the polymerization of acrylamide monomers. HPAM is created through a hydrolysis process that breaks down the polyacrylamide chains, producing a product with varying degrees of hydrolysis and molecular weight. Its unique properties make it a valuable compound in various industries, including oil and gas, water treatment, agriculture, and personal care.
1. Properties of Hydrolyzed Polyacrylamide
The structural characteristics of HPAM allow for a versatile range of applications. The extent of hydrolysis significantly influences its solubility, viscosity, and ion exchange properties. Hydrolyzed polyacrylamide is soluble in water and can form a gel-like consistency under certain conditions. The presence of hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions in the polymer structure facilitates its interactions with different substances, making it an effective agent in various formulations.
The degree of hydrolysis of HPAM can range from a few percent to over 90%, affecting its viscosity and interactions in various applications. Low degrees of hydrolysis lead to increased water solubility, while higher hydrolysis levels enhance its ability to interact with oppositely charged ions and particles, which can be beneficial in particular applications such as flocculation or enhanced oil recovery.
2. Applications in Oil and Gas Industry
One of the primary applications of hydrolyzed polyacrylamide is in the oil and gas industry, particularly during the process of enhanced oil recovery (EOR). HPAM acts as a thickening agent, helping to improve the mobility of water used in the extraction process. This enhances the dispersion of water and improves the oil recovery rate by reducing the water-oil interfacial tension. HPAM is also employed in drilling fluids, where its viscoelastic properties help control fluid loss and improve the stability of the borehole structure.
Moreover, HPAM serves as a stabilizer for the colloidal stability of emulsions used in various drilling applications, ensuring that the drilling performance is optimized while minimizing environmental impact.
3. Water Treatment and Environmental Applications
hydrolyzed polyacrylamide
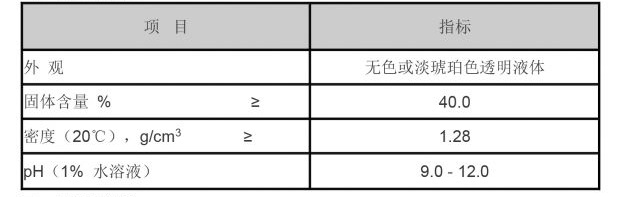
Hydrolyzed polyacrylamide is widely utilized in water treatment processes due to its excellent flocculating properties. In municipal wastewater treatment plants, HPAM is employed to aggregate and remove suspended solids from effluents. Its ability to form larger flocs improves the efficiency of sedimentation processes, leading to clearer water quality for discharge or further treatment.
In addition to municipal applications, HPAM is used in industrial wastewater treatment, helping industries meet their effluent discharge regulations. It is also explored for its potential in soil remediation efforts, where it can assist in binding contaminants, ultimately aiding in environmental cleanup strategies.
4. Agricultural Applications
HPAM is gaining traction in the agricultural sector, particularly as a soil conditioner and water retention agent. Its ability to improve soil structure enhances water infiltration and retention, making it beneficial for crop production, especially in arid regions. When HPAM is added to soil, it forms a gel-like substance that can hold significant amounts of water and nutrients, providing farmers with a more sustainable solution for irrigation.
Furthermore, HPAM enhances seed germination and plant growth by promoting better soil aeration and root development. As a biodegradable material, it aligns with sustainable agricultural practices and helps mitigate soil erosion.
5. Personal Care and Cosmetics
In the personal care industry, hydrolyzed polyacrylamide is used as a thickening agent in various cosmetic formulations, including creams, lotions, and gels. Its ability to enhance the texture and consistency of products while providing a soft feel on the skin has made it a popular ingredient. Additionally, HPAM's film-forming properties allow it to act as a moisture retention agent, improving the hydrating effects of skincare products.
Conclusion
Hydrolyzed polyacrylamide is a versatile polymer with a multitude of applications across diverse industries. Its unique properties facilitate its use in oil and gas extraction, water treatment, agriculture, and personal care products. As industries continue to innovate and seek sustainable solutions, HPAM’s role is likely to expand, contributing to efficiency and eco-friendliness in various processes. With ongoing research and development, hydrolyzed polyacrylamide stands as a testament to the potential of polymers in enhancing product performance and environmental sustainability.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





