PAM Flocculant Applications and Benefits in Water Treatment Processes
Understanding PAM Flocculants Applications and Benefits
Polyacrylamide (PAM) flocculants have emerged as a vital ingredient in various industrial processes, particularly in wastewater treatment, mining, and food processing. PAM, a synthetic polymer, is recognized for its exceptional ability to facilitate the aggregation of particles in liquids, making it an essential component in the flocculation process. This article delves into the properties, applications, and benefits of PAM flocculants.
What is PAM?
Polyacrylamide is a long-chain polymer formed through the polymerization of acrylamide monomers. It exists in various forms, including anionic, cationic, and non-ionic types, which can be customized depending on the specific application requirements. The unique molecular structure of PAM enhances its ability to interact with suspended solids in water, leading to their aggregation and subsequent removal.
Applications of PAM Flocculants
1. Wastewater Treatment One of the most prominent applications of PAM is in wastewater treatment. PAM flocculants are used to clarify water by promoting the aggregation of suspended particles, heavy metals, and organic matter. This is particularly beneficial in municipal and industrial wastewater treatment plants, where they aid in the separation of solids from liquids, making the treatment process more efficient.
2. Mining Industry In the mining sector, PAM flocculants are commonly employed in processes such as mineral separation, where they help in concentrating ores by settling unwanted materials. Additionally, they are used in tailings management, where the flocculants facilitate the consolidation of fine particles, reducing the environmental impact and improving the recoverability of valuable materials.
3. Food Processing PAM finds its way into the food industry as well. It is used in clarifying juices and wines, aiding in the removal of impurities and enhancing the overall quality of the final product. Moreover, in dairy processing, PAM can assist in the clarification of whey, providing a clearer and more appealing product.
4. Agriculture In agriculture, PAM flocculants can be beneficial in soil erosion control and water retention. When applied to soil, PAM enhances the aggregation of soil particles, improving water infiltration and nutrient retention. This can lead to increased productivity and sustainability in agricultural practices.
pam flocculant
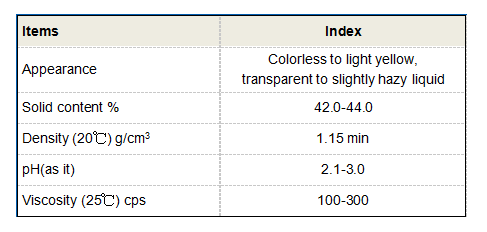
Benefits of PAM Flocculants
1. Efficiency One of the key advantages of PAM flocculants is their efficiency in removing particulate matter from liquids. Their high molecular weight and charge properties facilitate the bonding of particles, resulting in rapid sedimentation and reduced processing times.
2. Cost-Effectiveness PAM flocculants can significantly lower operational costs in treatment processes by reducing the need for additional chemicals and energy consumption. Their effectiveness in small dosages translates into substantial savings in various applications.
3. Environmental Impact Utilizing PAM flocculants can lead to less environmental degradation. By improving wastewater treatment processes, they help in compliance with environmental regulations and contribute to the preservation of water bodies by minimizing pollutant discharge.
4. Versatility The different types of PAM flocculants allow for customization based on the specific needs of a process. This versatility makes PAM suitable for a wide range of applications across different industries.
5. Enhanced Product Quality In food and beverage applications, PAM flocculants improve product clarity and quality, resulting in a better consumer experience. This can enhance brand reputation and customer satisfaction.
Conclusion
PAM flocculants play a crucial role in modern industrial processes by improving efficiency, reducing costs, and minimizing environmental impacts. Their diverse applications across wastewater treatment, mining, food processing, and agriculture highlight their importance in promoting sustainability and operational effectiveness. As industries continue to seek innovative solutions to their challenges, the use of PAM flocculants is likely to expand, contributing to more efficient and environmentally friendly processes.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





