Feb . 05, 2025 02:24
Back to list
partially hydrolysed polyacrylamide
Partially hydrolysed polyacrylamide (PHPA) is an innovative product that has revolutionized several industries due to its unique properties. Its primary application is in the petroleum industry, where it plays a vital role in enhanced oil recovery (EOR) processes. The effectiveness of PHPA in EOR operations stems from its ability to alter the viscosity of water used in the flooding process, thereby improving the displacement efficiency of oil from the reservoir.
Although partially hydrolysed polyacrylamide presents numerous benefits, its use is accompanied by some challenges. The environmental impact of its production and degradation continues to be a topic of research. As a result, manufacturers and researchers are collaboratively working on developing eco-friendly alternatives and establishing guidelines to minimize any adverse effects. Industry experts recommend a careful selection of PHPA grades to tailor its applications to specific operational needs. This customization ensures high efficiency and cost-effectiveness, aligning with the precise demands of each field. Continuous advancements in the formulation of PHPA are being pursued to extend its applicability while enhancing its performance across all industries. For organizations contemplating the integration of PHPA into their processes, it is crucial to consult with specialists who possess deep-seated knowledge about the compound’s properties and best practices for its application. Such expertise will fortify the reliability and effectiveness of PHPA, culminating in optimal operational outcomes. Overall, partially hydrolysed polyacrylamide stands as a testament to the intersection of chemical innovation and industrial demand. Its multifaceted applications underscore its value and position it as a critical contributor to industry-wide advancements. As its scopes expand and environmental solutions evolve, PHPA is set to sustain its significance, making it an indispensable component in future technological applications. The continued research and development of PHPA not only aim to enhance its applications but also to ensure its compliance with global environmental and safety standards. As industries evolve, PHPA’s role in promoting efficient and sustainable practices will remain pivotal, earning it an esteemed reputation among chemicals with transformative potential.

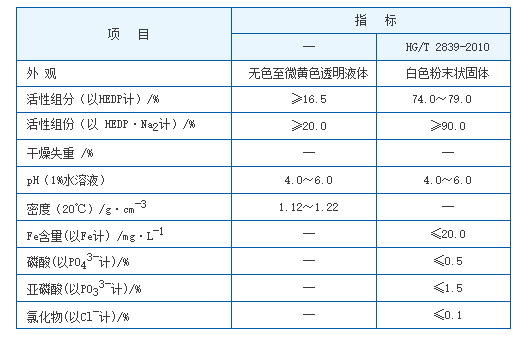
Although partially hydrolysed polyacrylamide presents numerous benefits, its use is accompanied by some challenges. The environmental impact of its production and degradation continues to be a topic of research. As a result, manufacturers and researchers are collaboratively working on developing eco-friendly alternatives and establishing guidelines to minimize any adverse effects. Industry experts recommend a careful selection of PHPA grades to tailor its applications to specific operational needs. This customization ensures high efficiency and cost-effectiveness, aligning with the precise demands of each field. Continuous advancements in the formulation of PHPA are being pursued to extend its applicability while enhancing its performance across all industries. For organizations contemplating the integration of PHPA into their processes, it is crucial to consult with specialists who possess deep-seated knowledge about the compound’s properties and best practices for its application. Such expertise will fortify the reliability and effectiveness of PHPA, culminating in optimal operational outcomes. Overall, partially hydrolysed polyacrylamide stands as a testament to the intersection of chemical innovation and industrial demand. Its multifaceted applications underscore its value and position it as a critical contributor to industry-wide advancements. As its scopes expand and environmental solutions evolve, PHPA is set to sustain its significance, making it an indispensable component in future technological applications. The continued research and development of PHPA not only aim to enhance its applications but also to ensure its compliance with global environmental and safety standards. As industries evolve, PHPA’s role in promoting efficient and sustainable practices will remain pivotal, earning it an esteemed reputation among chemicals with transformative potential.
Share
Next:
Latest news
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





