Jun . 13, 2024 11:06
Back to list
Phosphonates Essential compounds in water treatment and agriculture.
Phosphonates are a class of compounds that have gained significant attention in various scientific and industrial fields due to their unique properties and applications. These compounds contain a phosphorus atom directly bound to an organic moiety through a carbon-phosphorus bond, rendering them highly versatile and stable.
Phosphonates find their primary use as water treatment chemicals, where they act as scale inhibitors and corrosion inhibitors. Their ability to form strong complexes with calcium and other metal ions prevents the precipitation of minerals, thus inhibiting the formation of scales in cooling towers, boilers, and pipes. This is particularly crucial in industries like power generation, oil and gas, and HVAC systems, where maintaining clean water systems is paramount.
In the field of agriculture, phosphonates serve as effective fungicides and herbicides. For instance, fosetyl-Al, a widely used phosphonate, is a systemic fungicide that combats a range of plant diseases. It interferes with the metabolism of fungi, leading to their death, while being relatively non-toxic to plants and mammals.
Pharmaceuticals also utilize phosphonates, particularly in the development of antiviral drugs. Famciclovir, a popular anti-herpes medication, contains a phosphonoacetic acid derivative, which inhibits viral DNA synthesis. Similarly, adefovir and tenofovir, both used in the treatment of HIV, are phosphonate prodrugs that are converted into active phosphorylated forms within cells.
In the realm of materials science, phosphonates contribute to the creation of advanced materials
In the realm of materials science, phosphonates contribute to the creation of advanced materials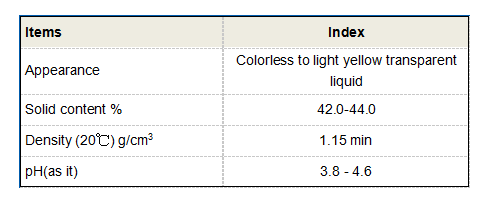 In the realm of materials science, phosphonates contribute to the creation of advanced materials
In the realm of materials science, phosphonates contribute to the creation of advanced materials
In the realm of materials science, phosphonates contribute to the creation of advanced materials
In the realm of materials science, phosphonates contribute to the creation of advanced materials phosphonate . They can be used to functionalize polymers, enhancing their stability, flame retardancy, and adhesion properties. For example, phosphonate-functionalized polyolefins have been employed in the production of high-performance coatings for various surfaces.
Furthermore, phosphonates play a role in environmental protection. As chelating agents, they aid in the removal of heavy metals from contaminated soils and waters, contributing to remediation efforts. They also find use in the recovery of precious metals from industrial waste streams.
Despite their wide usage, concerns over the potential environmental impact of phosphonates have emerged. Their persistence in the environment and potential interference with natural phosphorus cycles warrant further research and development of more eco-friendly alternatives.
In conclusion, phosphonates, with their diverse range of applications, are indispensable in many sectors. From water treatment and agriculture to pharmaceuticals and materials science, they demonstrate the power of chemistry in addressing real-world challenges. However, it's essential to continue researching their environmental implications and strive for sustainable solutions.
phosphonate . They can be used to functionalize polymers, enhancing their stability, flame retardancy, and adhesion properties. For example, phosphonate-functionalized polyolefins have been employed in the production of high-performance coatings for various surfaces.
Furthermore, phosphonates play a role in environmental protection. As chelating agents, they aid in the removal of heavy metals from contaminated soils and waters, contributing to remediation efforts. They also find use in the recovery of precious metals from industrial waste streams.
Despite their wide usage, concerns over the potential environmental impact of phosphonates have emerged. Their persistence in the environment and potential interference with natural phosphorus cycles warrant further research and development of more eco-friendly alternatives.
In conclusion, phosphonates, with their diverse range of applications, are indispensable in many sectors. From water treatment and agriculture to pharmaceuticals and materials science, they demonstrate the power of chemistry in addressing real-world challenges. However, it's essential to continue researching their environmental implications and strive for sustainable solutions.
 In the realm of materials science, phosphonates contribute to the creation of advanced materials
In the realm of materials science, phosphonates contribute to the creation of advanced materials
In the realm of materials science, phosphonates contribute to the creation of advanced materials
In the realm of materials science, phosphonates contribute to the creation of advanced materials phosphonate . They can be used to functionalize polymers, enhancing their stability, flame retardancy, and adhesion properties. For example, phosphonate-functionalized polyolefins have been employed in the production of high-performance coatings for various surfaces.
Furthermore, phosphonates play a role in environmental protection. As chelating agents, they aid in the removal of heavy metals from contaminated soils and waters, contributing to remediation efforts. They also find use in the recovery of precious metals from industrial waste streams.
Despite their wide usage, concerns over the potential environmental impact of phosphonates have emerged. Their persistence in the environment and potential interference with natural phosphorus cycles warrant further research and development of more eco-friendly alternatives.
In conclusion, phosphonates, with their diverse range of applications, are indispensable in many sectors. From water treatment and agriculture to pharmaceuticals and materials science, they demonstrate the power of chemistry in addressing real-world challenges. However, it's essential to continue researching their environmental implications and strive for sustainable solutions.
phosphonate . They can be used to functionalize polymers, enhancing their stability, flame retardancy, and adhesion properties. For example, phosphonate-functionalized polyolefins have been employed in the production of high-performance coatings for various surfaces.
Furthermore, phosphonates play a role in environmental protection. As chelating agents, they aid in the removal of heavy metals from contaminated soils and waters, contributing to remediation efforts. They also find use in the recovery of precious metals from industrial waste streams.
Despite their wide usage, concerns over the potential environmental impact of phosphonates have emerged. Their persistence in the environment and potential interference with natural phosphorus cycles warrant further research and development of more eco-friendly alternatives.
In conclusion, phosphonates, with their diverse range of applications, are indispensable in many sectors. From water treatment and agriculture to pharmaceuticals and materials science, they demonstrate the power of chemistry in addressing real-world challenges. However, it's essential to continue researching their environmental implications and strive for sustainable solutions. Share
Latest news
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





