Polyacrylamide
Polyacrylamide (PAM) is a versatile synthetic polymer that has found widespread application across various industries due to its unique properties. Composed of acrylamide monomers, polyacrylamide is known for its ability to absorb water, form gels, and serve as a flocculating agent. Its chemical structure provides an extensive surface area, making it effective in various formulations and processes.
One of the primary uses of polyacrylamide is in the field of water treatment
. PAM is utilized as a flocculant to enhance the removal of suspended particles in wastewater. When polyacrylamide is added to water, it helps agglomerate fine particles into larger clusters that can be easily removed through sedimentation or filtration. This is crucial for municipal water treatment plants, industrial processes, and even in agricultural runoff management, where water quality is a significant concern.In the oil and gas industry, polyacrylamide plays a vital role in enhancing oil recovery. By injecting PAM into oil reservoirs, the viscosity of water is increased, helping to push the oil towards extraction points more efficiently. This technique, known as enhanced oil recovery (EOR), significantly boosts the amount of oil that can be feasibly extracted from reservoirs, improving the economics of oil production and contributing to energy sustainability.
Polyacrylamide is also widely used in the field of biomedicine. Its ability to form hydrogels makes it ideal for applications such as drug delivery systems, tissue engineering, and wound dressings. The controlled release properties of polyacrylamide-based hydrogels allow for the sustained delivery of therapeutic agents, enhancing their efficacy while minimizing side effects. Additionally, its biocompatibility makes it a suitable material for direct contact with biological tissues.
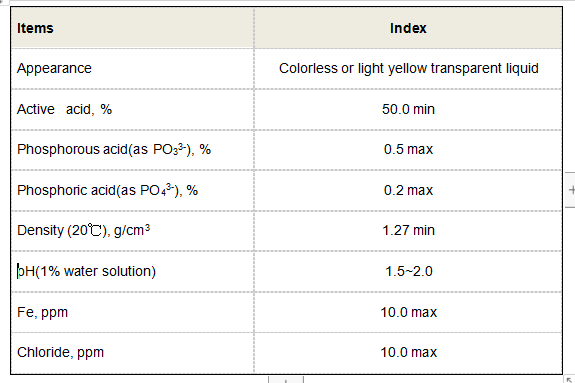
polyacrylamide is a
Another important application of polyacrylamide is in the agricultural sector. Farmers and agronomists utilize PAM as a soil conditioner, improving soil structure and water retention. When applied to sandy soils, PAM can increase the soil's ability to hold moisture, thereby reducing irrigation needs and promoting healthier plant growth. This property is particularly advantageous in arid regions where water scarcity is an ongoing challenge.
Despite its numerous benefits, it is essential to address safety concerns related to polyacrylamide. Acrylamide, the monomer from which it is synthesized, is known to be a potential neurotoxin and carcinogen. Therefore, strict regulations govern the use of polyacrylamide, especially in food-related applications. The industry has made strides in developing safer variants, including non-toxic and biodegradable forms of polyacrylamide, which mitigate health risks while retaining functionality.
In conclusion, polyacrylamide is a remarkable polymer with diverse applications across various domains, including water treatment, oil recovery, biomedical fields, and agriculture. Its unique properties make it an invaluable tool in addressing key challenges in these industries. While safety concerns regarding its precursor, acrylamide, must be taken seriously, ongoing research and development are focused on creating safer alternatives. As industries continue to innovate, the role of polyacrylamide is expected to expand, contributing significantly to technological advancements and sustainability efforts worldwide.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





