Applications and Benefits of Polyacrylamide Polymer in Various Industries
Understanding Polyacrylamide Polymer Properties, Applications, and Benefits
Polyacrylamide (PAM) is a synthetic polymer that finds widespread application across various industries due to its unique chemical properties and versatility. Produced by the polymerization of acrylamide monomers, polyacrylamide comes in different forms, including anionic, cationic, and nonionic. This article delves into the structure, properties, applications, and benefits of polyacrylamide polymers.
Structure and Properties
Polyacrylamide is a white, water-soluble polymer that comprises long chains of acrylamide units. The structure allows it to absorb significant amounts of water, contributing to its gel-like consistency. One of the most notable features of PAM is its ability to form viscoelastic solutions and gels, which can enhance the thickness and stability of various formulations.
Polyacrylamide can exhibit different ionic characteristics based on its formulation. Anionic polyacrylamide, which bears a negative charge, is effective in flocculation processes, where it promotes the agglomeration of suspended particles. Cationic polyacrylamide, with positive charges, is beneficial in applications such as water treatment and paper manufacturing, where it enhances formation and retention. Nonionic polyacrylamide is neutral and is often used in contexts where ionic interactions are either unwanted or need to be minimized.
Applications in Various Industries
Polyacrylamide has a broad range of applications across multiple sectors, proving its utility and effectiveness
1. Water Treatment One of the primary uses of polyacrylamide is in the treatment of municipal and industrial wastewater. The polymer acts as a flocculant, facilitating the removal of suspended solids, colloids, and other impurities, thereby improving water clarity and quality. Its efficiency in sedimentation and filtration makes it an essential component in the water treatment industry.
2. Agriculture In the agricultural sector, polyacrylamide is employed as a soil conditioner. It improves soil structure, enhancing moisture retention and reducing erosion. The use of PAM helps increase crop yields and reduces the need for frequent irrigation, making it a valuable tool for sustainable farming practices.
polyacrylamide polymer
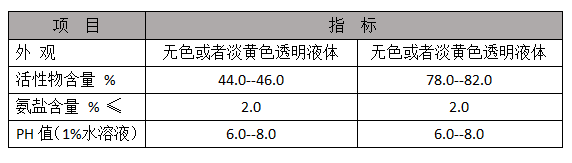
3. Mining and Mineral Processing In the mining industry, polyacrylamide is utilized to facilitate the separation of minerals from ore. The polymer enhances the flocculation process, allowing for more efficient recovery of minerals such as gold and copper. This application not only optimizes resource extraction but also minimizes environmental impacts.
4. Oil Recovery Polyacrylamide is also used in enhanced oil recovery techniques. The polymer enhances the viscosity of water injections used during secondary and tertiary oil recovery methods, improving the displacement of oil and increasing overall yield.
5. Personal Care Products In the cosmetics industry, polyacrylamide is an essential ingredient in various formulations, including lotions, gels, and creams. It acts as a thickening agent, stabilizer, and emulsifier, improving the texture and application of personal care products.
Benefits of Polyacrylamide
The use of polyacrylamide offers numerous advantages. Its ability to form hydrogels is beneficial for controlled delivery systems in pharmaceuticals and agriculture. Furthermore, polyacrylamide’s biodegradability, especially in its crosslinked form, makes it an environmentally friendly option compared to other synthetic polymers.
Moreover, the versatility of polyacrylamide allows it to be tailored for specific applications. Its chemical composition can be adjusted to meet particular requirements, making it a highly customizable solution for industries ranging from healthcare to manufacturing.
Conclusion
Polyacrylamide is a remarkable polymer with diverse applications that span industries like water treatment, agriculture, mining, oil recovery, and personal care. Its unique properties, including water solubility, versatility in ionic form, and ability to enhance processes, underscore its significance in modern applications. As industries continue to seek efficient and sustainable solutions, the role of polyacrylamide will likely expand, making it a vital component in innovative practices across various fields.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





