polyacrylamide use
The Versatile Uses of Polyacrylamide in Various Industries
Polyacrylamide (PAM) is a synthetic polymer widely utilized across various industries due to its unique properties, making it an essential compound in numerous applications. Composed of acrylamide monomers, this water-soluble polymer has garnered attention for its ability to improve water retention, enhance soil quality, and facilitate efficient separation processes.
One of the most notable applications of polyacrylamide is in agriculture. Farmers and agricultural specialists often use PAM to improve soil structure and enhance moisture retention. By adding polyacrylamide to the soil, it helps to create a gel-like substance that holds moisture, which is especially beneficial in arid regions. This enhancement leads to increased crop yields and reduced irrigation needs, ultimately promoting sustainable farming practices.
The Versatile Uses of Polyacrylamide in Various Industries
Additionally, polyacrylamide is indispensable in the oil and gas industry. It is often employed in enhanced oil recovery (EOR) processes. By injecting PAM into oil reservoirs, the polymer reduces the viscosity of the oil, allowing it to flow more freely through the geological formations. This enhancement maximizes oil recovery rates and minimizes the environmental impact of extraction processes.
polyacrylamide use
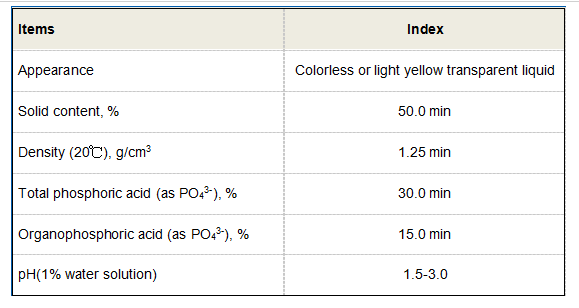
Furthermore, polyacrylamide finds use in the paper industry, where it acts as a retention aid and improves the efficiency of the paper manufacturing process. It helps in retaining fine fibers and fillers in the paper pulp, thus enhancing the quality and strength of the final product. The incorporation of PAM leads to more efficient production, reducing waste and costs for manufacturers.
In cosmetics and personal care products, Polyacrylamide functions as a thickening agent and film-forming agent. It provides the desired texture and stability in lotions and creams, ensuring a smooth application and an appealing end product.
Despite its numerous benefits, it is essential to handle polyacrylamide with care, as it is derived from acrylamide, a compound recognized for its potential health risks. Therefore, regulatory measures and safety protocols are crucial in industries using PAM to mitigate any risk to human health and the environment.
In conclusion, polyacrylamide is a remarkably versatile polymer with applications spanning agriculture, water treatment, oil recovery, paper production, and cosmetics. Its ability to enhance processes and improve end products makes it a valuable asset across multiple sectors, underscoring its significance in modern industry.
-
Pbtc Scale InhibitorPBTC: A Scale Protector for Industrial Water TreatmentNewsAug.05,2025
-
Organic Phosphonate: An Efficient Defender in the Field of Scale InhibitionNewsAug.05,2025
-
Hydrolyzed Polymaleic Anhydride: Green Pioneer in Scale Inhibition FieldNewsAug.05,2025
-
PAPEMP Polyamino Polyether Methylene Phosphonic Acid For SaleNewsAug.05,2025
-
Flocculant Water Treatment: A Pioneer in Purification in the Field of Water TreatmentNewsAug.05,2025
-
Benzyl Isothiazolinone: An Efficient and Broad-Spectrum Antibacterial Protective GuardNewsAug.05,2025





