Jun . 12, 2024 15:04
Back to list
Polyacrylic acid is a prominent example of polycarboxylic acids.
Understanding Polycarboxylic Acids A Comprehensive Overview
Polycarboxylic acids, also known as polyacids, are chemical compounds characterized by the presence of multiple carboxylic acid groups (-COOH) in their molecular structure. These compounds play significant roles in various scientific and industrial applications due to their unique properties and reactivity. Some common examples of polycarboxylic acids include citric acid, oxalic acid, tartaric acid, and succinic acid.
Citric acid, for instance, is a tricarboxylic acid found naturally in citrus fruits like lemons and oranges. It is widely used as a flavoring agent, preservative, and chelating agent in the food industry. Its ability to bind with metal ions makes it effective in removing impurities and preventing corrosion.
Oxalic acid, a dicarboxylic acid, is another well-known example. It exists in many plants and is used industrially for bleaching, cleaning, and rust removal. Its high reactivity with metals forms insoluble oxalate salts, which explains its use in rust treatment.
Tartaric acid, a dicarboxylic acid, is commonly found in grapes and plays a crucial role in winemaking. In addition, it has uses in baking, as a food additive, and in the pharmaceutical industry due to its sour taste and ability to stabilize emulsions In addition, it has uses in baking, as a food additive, and in the pharmaceutical industry due to its sour taste and ability to stabilize emulsions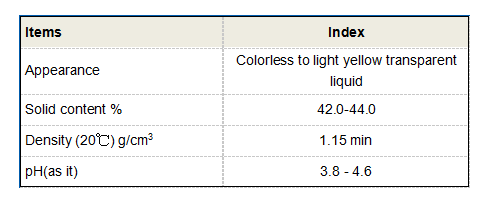 In addition, it has uses in baking, as a food additive, and in the pharmaceutical industry due to its sour taste and ability to stabilize emulsions In addition, it has uses in baking, as a food additive, and in the pharmaceutical industry due to its sour taste and ability to stabilize emulsions
In addition, it has uses in baking, as a food additive, and in the pharmaceutical industry due to its sour taste and ability to stabilize emulsions In addition, it has uses in baking, as a food additive, and in the pharmaceutical industry due to its sour taste and ability to stabilize emulsions polycarboxylic acid examples.
Succinic acid, a four-carboxylic acid, is a key intermediate in the citric acid cycle, a fundamental metabolic pathway in living organisms. It is also produced industrially on a large scale and finds applications in the production of polymers, drugs, and food additives.
Polycarboxylic acids have diverse applications due to their acidic properties, chelating capacity, and ability to form esters and salts. They are employed in chemical synthesis, as pH regulators, in water treatment processes, and as antioxidants. In medicine, they are used in drug formulations due to their buffering capabilities. Moreover, they are essential in the development of environmentally friendly technologies, such as in the production of bio-based plastics.
In conclusion, polycarboxylic acids are versatile compounds with a broad range of applications across different sectors. Their significance lies not only in their chemical properties but also in their potential to contribute to sustainable practices and green chemistry initiatives. As research continues to explore new uses and understand the complexities of these acids, their importance in science and industry is expected to grow further.
polycarboxylic acid examples.
Succinic acid, a four-carboxylic acid, is a key intermediate in the citric acid cycle, a fundamental metabolic pathway in living organisms. It is also produced industrially on a large scale and finds applications in the production of polymers, drugs, and food additives.
Polycarboxylic acids have diverse applications due to their acidic properties, chelating capacity, and ability to form esters and salts. They are employed in chemical synthesis, as pH regulators, in water treatment processes, and as antioxidants. In medicine, they are used in drug formulations due to their buffering capabilities. Moreover, they are essential in the development of environmentally friendly technologies, such as in the production of bio-based plastics.
In conclusion, polycarboxylic acids are versatile compounds with a broad range of applications across different sectors. Their significance lies not only in their chemical properties but also in their potential to contribute to sustainable practices and green chemistry initiatives. As research continues to explore new uses and understand the complexities of these acids, their importance in science and industry is expected to grow further.
 In addition, it has uses in baking, as a food additive, and in the pharmaceutical industry due to its sour taste and ability to stabilize emulsions In addition, it has uses in baking, as a food additive, and in the pharmaceutical industry due to its sour taste and ability to stabilize emulsions
In addition, it has uses in baking, as a food additive, and in the pharmaceutical industry due to its sour taste and ability to stabilize emulsions In addition, it has uses in baking, as a food additive, and in the pharmaceutical industry due to its sour taste and ability to stabilize emulsions polycarboxylic acid examples.
Succinic acid, a four-carboxylic acid, is a key intermediate in the citric acid cycle, a fundamental metabolic pathway in living organisms. It is also produced industrially on a large scale and finds applications in the production of polymers, drugs, and food additives.
Polycarboxylic acids have diverse applications due to their acidic properties, chelating capacity, and ability to form esters and salts. They are employed in chemical synthesis, as pH regulators, in water treatment processes, and as antioxidants. In medicine, they are used in drug formulations due to their buffering capabilities. Moreover, they are essential in the development of environmentally friendly technologies, such as in the production of bio-based plastics.
In conclusion, polycarboxylic acids are versatile compounds with a broad range of applications across different sectors. Their significance lies not only in their chemical properties but also in their potential to contribute to sustainable practices and green chemistry initiatives. As research continues to explore new uses and understand the complexities of these acids, their importance in science and industry is expected to grow further.
polycarboxylic acid examples.
Succinic acid, a four-carboxylic acid, is a key intermediate in the citric acid cycle, a fundamental metabolic pathway in living organisms. It is also produced industrially on a large scale and finds applications in the production of polymers, drugs, and food additives.
Polycarboxylic acids have diverse applications due to their acidic properties, chelating capacity, and ability to form esters and salts. They are employed in chemical synthesis, as pH regulators, in water treatment processes, and as antioxidants. In medicine, they are used in drug formulations due to their buffering capabilities. Moreover, they are essential in the development of environmentally friendly technologies, such as in the production of bio-based plastics.
In conclusion, polycarboxylic acids are versatile compounds with a broad range of applications across different sectors. Their significance lies not only in their chemical properties but also in their potential to contribute to sustainable practices and green chemistry initiatives. As research continues to explore new uses and understand the complexities of these acids, their importance in science and industry is expected to grow further. Share
Latest news
-
Understanding Polycarboxylic Acids: Properties, Applications, and Future PotentialNewsJul.28,2025
-
Scale Inhibitor Explained: How to Protect Your System from Limescale and Hard Water DamageNewsJul.28,2025
-
Scale and Corrosion Inhibitors: Essential Chemicals for Industrial Water System ProtectionNewsJul.28,2025
-
Polyaspartic Acid: A Biodegradable Polymer for Sustainable ChemistryNewsJul.28,2025
-
Isothiazolinones: A Versatile Antimicrobial Class with Industrial Power and Regulatory ChallengesNewsJul.28,2025
-
A Deep Dive into 2-Phosphonobutane-1,2,4-Tricarboxylic Acid (PBTC)NewsJul.28,2025





