polyaluminium chloride solution
Understanding Poly-Aluminium Chloride Solution Applications and Benefits
Poly-Aluminium Chloride (PAC) is an inorganic polymer that is widely used in water treatment processes. As a versatile coagulant, PAC has gained popularity due to its effectiveness in addressing various water quality issues while offering several advantages over traditional coagulants such as aluminum sulfate. This article delves into the properties of PAC, its applications, and the benefits it brings to water treatment facilities.
What is Poly-Aluminium Chloride?
Poly-Aluminium Chloride is a chemical compound that consists of a combination of aluminium ions and chloride ions. It appears as a yellowish white powder or as a liquid solution. When dissolved in water, PAC decomposes to form a series of hydrolyzed aluminium species which contribute to its coagulation properties. The polymeric structure enhances its efficiency, allowing it to stabilize suspensions in water and promote the aggregation of small particles into larger flocs that can be easily removed from water systems.
Applications of PAC
The primary application of Poly-Aluminium Chloride is in the treatment of drinking water, wastewater, and industrial effluents. In drinking water treatment, PAC effectively removes suspended solids, organic matter, and pathogens, thus improving water clarity and safety. Its ability to work efficiently over a broad pH range makes it suitable for various water sources, including surface water and groundwater.
In wastewater treatment, PAC plays a crucial role in the removal of phosphates and heavy metals, contributing to compliance with environmental regulations. It is particularly beneficial in treating wastewater from industries that generate high levels of particulates or organic pollutants, such as food processing, textiles, and paper manufacturing. Additionally, PAC is employed in sludge dewatering processes, enhancing the removal of water from sludge and thereby reducing disposal costs.
PAC is also utilized in the paper industry as a retention aid, promoting the retention of fibrous materials within the paper-making process. This application can lead to improved efficiency and reduced waste, making the production of paper more sustainable.
polyaluminium chloride solution
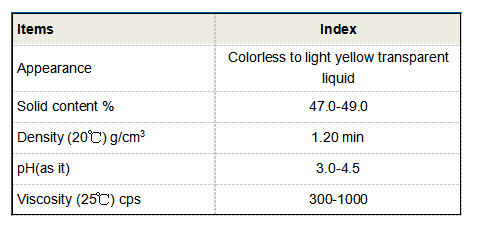
Benefits of Using Poly-Aluminium Chloride
The use of PAC in water treatment offers numerous benefits. Firstly, PAC is known for its superior coagulation performance compared to traditional coagulants. This allows for lower dosage rates, which not only cuts costs but also minimizes the handling and storage challenges associated with purchasing larger quantities of chemicals.
Secondly, PAC generates less sludge compared to other coagulants. This characteristic is particularly advantageous for wastewater treatment facilities, as it reduces the frequency of sludge disposal and can lead to lower operational costs.
Moreover, PAC improves the efficiency of filtration processes. The larger flocs produced through the coagulation process enhance the filtration rate, resulting in quicker processing times and better-quality water.
Another significant benefit of PAC is its effectiveness in a wide range of pH levels and temperatures, thus providing flexibility in various sourcing conditions. Its versatility allows operators to adapt to changing water quality without the need for frequent adjustments or additional chemicals.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Poly-Aluminium Chloride solution presents a powerful tool for water treatment facilities. Its unique properties, combined with its versatility and cost-effectiveness, make it an ideal choice for managing water quality in drinking water, wastewater, and industrial applications. As the demand for clean water continues to grow globally, PAC will play an essential role in meeting these challenges, ensuring access to safe potable water while mitigating environmental impacts.
-
Understanding Polycarboxylic Acids: Properties, Applications, and Future PotentialNewsJul.28,2025
-
Scale Inhibitor Explained: How to Protect Your System from Limescale and Hard Water DamageNewsJul.28,2025
-
Scale and Corrosion Inhibitors: Essential Chemicals for Industrial Water System ProtectionNewsJul.28,2025
-
Polyaspartic Acid: A Biodegradable Polymer for Sustainable ChemistryNewsJul.28,2025
-
Isothiazolinones: A Versatile Antimicrobial Class with Industrial Power and Regulatory ChallengesNewsJul.28,2025
-
A Deep Dive into 2-Phosphonobutane-1,2,4-Tricarboxylic Acid (PBTC)NewsJul.28,2025





