polyaluminum chloride solution
Understanding Polyaluminum Chloride Solution Composition, Applications, and Benefits
Polyaluminum chloride (PAC) is an aluminum-based coagulant commonly used in water treatment processes. This solution consists of polymerized aluminum ions (Al3+) and hydroxide ions (OH-), making it a versatile option for purifying drinking water, treating wastewater, and various industrial applications. Due to its effectiveness and lower dosage requirements compared to traditional coagulants, PAC has gained significant popularity in recent years.
Composition and Properties
PAC is produced by the reaction of aluminum hydroxide with hydrochloric acid, resulting in a diverse range of polymeric structures. The molecular weight of PAC can vary significantly, which influences its coagulation properties. Generally, PAC solutions can contain 10-30% aluminum oxide (Al2O3), depending on the intended application.
The unique structure of PAC enables it to form large flocs that can effectively trap and remove suspended particles, colloids, and organic matter from water. This characteristic makes PAC particularly advantageous in situations where high turbidity levels are present in the water source. Additionally, PAC operates efficiently across a wide pH range, usually between 4 to 8, making it suitable for various environmental conditions.
Applications in Water Treatment
One of the primary uses of PAC is in municipal water treatment facilities, where it plays a crucial role in the coagulation and flocculation processes. When PAC is added to raw water, it neutralizes the electric charges on particles, facilitating their aggregation into larger masses known as flocs. These flocs can then be easily removed through sedimentation or filtration, resulting in cleaner, safer water for consumption.
polyaluminum chloride solution
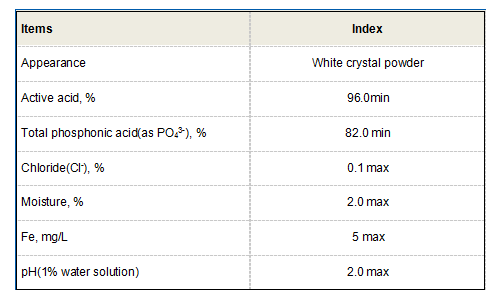
In wastewater treatment, PAC effectively reduces biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) and total suspended solids (TSS), making it easier to meet regulatory standards. It is particularly useful in treating industrial wastewater, where metal ions and other contaminants can complicate the treatment process.
Benefits of Using Polyaluminum Chloride
One of the most significant advantages of using PAC is its efficiency at lower dosages compared to traditional coagulants such as alum (aluminum sulfate). This results in reduced chemical costs and minimizes sludge production, leading to a more sustainable treatment process. The lower sludge volume also translates to lower disposal costs and environmental impacts.
Moreover, PAC produces clearer water, enhancing the overall quality of treated effluent. Its ability to work effectively at varying pH levels allows operators greater flexibility in managing water treatment processes under different conditions. Additionally, PAC is less corrosive than some other coagulants, reducing equipment wear and prolonging the life of treatment facilities.
Conclusion
Polyaluminum chloride solution has emerged as a powerful tool in the field of water treatment due to its effective coagulation properties and wide range of applications. Its ability to operate efficiently at lower dosages not only saves costs but also benefits the environment by minimizing sludge production. As the demand for clean water continues to rise alongside increasing regulatory pressures on wastewater treatment, PAC is poised to remain a valuable asset in modern water management strategies. By understanding the composition, applications, and benefits of polyaluminum chloride, stakeholders in the water treatment industry can make informed decisions that improve both the quality of water and the sustainability of treatment processes.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





