polycarboxylic
Understanding Polycarboxylic Acids Properties, Applications, and Significance
Polycarboxylic acids, a class of organic compounds characterized by the presence of two or more carboxyl (-COOH) functional groups, play a crucial role in various chemical processes and industrial applications. These compounds are integral to many biological functions and are widely utilized in the synthesis of polymers, pharmaceuticals, and as additives in numerous products.
Structure and Properties
The fundamental structure of polycarboxylic acids consists of carbon chains with multiple carboxyl groups attached. This unique feature contributes to their distinctive properties, including high acidity and the ability to form salts and esters. The presence of multiple carboxyl groups not only enhances the compound's reactivity but also allows for extensive intermolecular hydrogen bonding, which can significantly affect their physical properties such as solubility and melting point.
The acidity of polycarboxylic acids is typically higher than that of monocarboxylic acids due to the electron-withdrawing effects of the neighboring carboxyl groups. This feature makes them effective in various chemical reactions, including esterification and amidation. Additionally, the multiple functional groups can interact with metal ions, leading to applications in chelation and catalysis.
Common Examples
There are several well-known polycarboxylic acids, each with its unique properties and applications. Citric acid, found naturally in citrus fruits, is perhaps the most recognized polycarboxylic acid. It has three carboxyl groups, which contribute to its role as a natural preservative and flavoring agent in the food industry. Moreover, citric acid is used in the cosmetic and pharmaceutical industries due to its ability to adjust pH and act as a chelating agent.
Another example is oxalic acid, which contains two carboxyl groups and is found in various vegetables. Oxalic acid is often used as a cleaning agent and a reducing agent in chemical synthesis. Furthermore, it plays a significant role in organic chemistry as a building block for more complex reactions and synthesis.
Maleic acid, with its two carboxylic groups, is another polycarboxylic compound significant in industry. It is used to produce polymers like polyethylene terephthalate (PET), which is extensively used in plastic bottles and fabrics. Maleic anhydride, its derivative, is crucial in producing resins and coatings, showcasing the versatility of polycarboxylic acids in various industrial applications.
polycarboxylic
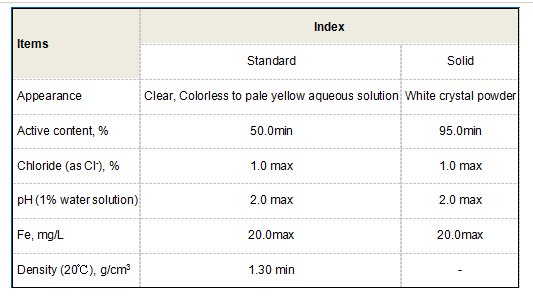
Industrial Applications
The industrial significance of polycarboxylic acids cannot be overstated. One of their primary uses is in the production of thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers. Polycarboxylic acids can act as monomers in the synthesis of polyesters and polyamides, which are crucial materials in textiles, automotive parts, and packaging.
In the construction industry, polycarboxylic acids are utilized as superplasticizers in concrete production. These superplasticizers enhance the workability and flow of concrete mixtures, allowing for reduced water content without sacrificing strength, thereby improving the efficiency of construction processes.
Moreover, polycarboxylic acids are employed in water treatment as chelating agents, binding metal ions and preventing scale formation. This property is essential for maintaining the efficiency and longevity of industrial equipment and ensuring the purity of water used in various applications.
Medical and Biological Importance
In addition to their industrial applications, polycarboxylic acids have significant biological relevance. They participate in metabolic pathways and play essential roles in various physiological processes. For instance, citric acid is a key component of the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle), which is fundamental for energy production in living organisms.
Furthermore, the medical field has embraced polycarboxylic acids in drug formulation and delivery systems. Their ability to form complexes with metal ions and organic molecules can be harnessed to improve the bioavailability of certain drugs, enhancing therapeutic outcomes.
Conclusion
Polycarboxylic acids are a diverse and impactful class of compounds that contribute significantly to various industries and biological processes. Their unique structures and properties enable a wide range of applications, from food preservation to advanced polymer production and medical formulations. As research advances, the potential of polycarboxylic acids continues to expand, highlighting their importance in both scientific and practical domains. Understanding these compounds is crucial for leveraging their benefits while addressing the challenges and opportunities they present in modern chemistry and industry.
-
Pbtc Scale InhibitorPBTC: A Scale Protector for Industrial Water TreatmentNewsAug.05,2025
-
Organic Phosphonate: An Efficient Defender in the Field of Scale InhibitionNewsAug.05,2025
-
Hydrolyzed Polymaleic Anhydride: Green Pioneer in Scale Inhibition FieldNewsAug.05,2025
-
PAPEMP Polyamino Polyether Methylene Phosphonic Acid For SaleNewsAug.05,2025
-
Flocculant Water Treatment: A Pioneer in Purification in the Field of Water TreatmentNewsAug.05,2025
-
Benzyl Isothiazolinone: An Efficient and Broad-Spectrum Antibacterial Protective GuardNewsAug.05,2025





