polymaleic anhydride
Polymaleic Anhydride Structure, Applications, and Benefits
Polymaleic anhydride (PMA) is a synthetic polymer that belongs to the family of maleic anhydride-based compounds. It is derived from the polymerization of maleic anhydride, a colorless, solid organic compound well-known for its ability to undergo various chemical reactions. PMA is characterized by its unique structure, properties, and versatile applications, making it a significant material in different industries.
The structure of polymaleic anhydride consists of repeating units of the maleic anhydride molecule, resulting in a polymer with a robust backbone. The polymerization process can be achieved through various methods, including free radical polymerization or ring-opening polymerization, leading to variations in molecular weight and chain length. The inherent properties of PMA include its solubility in polar solvents, thermal stability, and the ability to form gels and films, which enhances its usability in various applications.
One of the most notable applications of PMA is in the field of water treatment. Due to its excellent chelating abilities, PMA is employed to bind and remove heavy metals and other contaminants from water. The polymer's ability to sequester metal ions helps ensure that water resources meet safety standards and are protected from environmental pollutants. This application is particularly important in industries such as mining and manufacturing, where water sources are at risk of contamination.
polymaleic anhydride
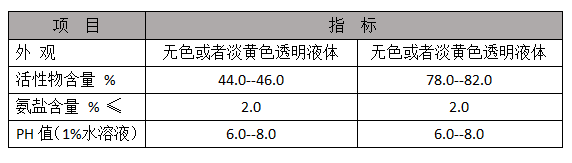
In addition to water treatment, polymaleic anhydride finds usage in the formulation of household and industrial cleaning products. Its ability to improve the performance of surfactants makes it an essential ingredient in detergents and cleaners. PMA aids in the dispersion of soils and enhances the overall cleaning efficiency, which is vital in both domestic and commercial settings.
Moreover, PMA serves as a valuable component in the production of adhesives and sealants. Its versatile chemical structure allows for modifications that can enhance adhesive properties, enabling it to bond various surfaces effectively. This feature is beneficial in numerous applications, from construction to automotive manufacturing, where strong adhesion is critical for performance and durability.
The pharmaceutical industry also leverages polymaleic anhydride for drug delivery systems. PMA can be modified to create nanocarriers that encapsulate drugs, allowing for controlled release and improved bioavailability. This application opens new avenues in the treatment of various diseases, as it enables targeted therapy while minimizing side effects.
In summary, polymaleic anhydride is a multi-functional polymer with a range of applications across several industries, including water treatment, cleaning products, adhesives, and pharmaceuticals. Its unique structure provides it with essential properties, making it a significant material in formulations that require effectiveness and efficiency. The ongoing research and development in modifying PMA further enhance its potential, paving the way for innovative solutions to meet the evolving needs of various sectors. As environmental concerns and technological advancements continue to rise, the role of polymaleic anhydride is expected to grow, offering sustainable and efficient materials for a better future.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





