scale and corrosion inhibitor
Scale and Corrosion Inhibitors Essential Tools for Industrial Efficiency
In numerous industrial processes, particularly those involving water systems, the dual menace of scale and corrosion presents significant operational challenges. These issues not only compromise the efficiency of the systems but also lead to costly downtime and increased maintenance expenses. To combat these problems, the implementation of scale and corrosion inhibitors has emerged as a crucial strategy for enhancing the longevity and reliability of equipment.
Understanding Scale and Corrosion
Scale primarily consists of mineral deposits that form on surfaces within water systems, often due to the presence of hard water. These deposits can accumulate in boilers, heat exchangers, and pipelines, significantly hindering fluid flow and thermal efficiency. On the other hand, corrosion refers to the gradual deterioration of materials, often metals, caused by chemical reactions with the environment, particularly moisture and oxygen. Both issues can result in reduced operational efficiency and increased energy consumption, making it imperative to find effective solutions.
The Role of Inhibitors
Scale and corrosion inhibitors are chemical compounds designed to prevent or mitigate these detrimental effects. Their application varies across industries, including power generation, oil and gas, and manufacturing. These inhibitors function through different mechanisms, tailored to the specific needs of the system in which they are employed.
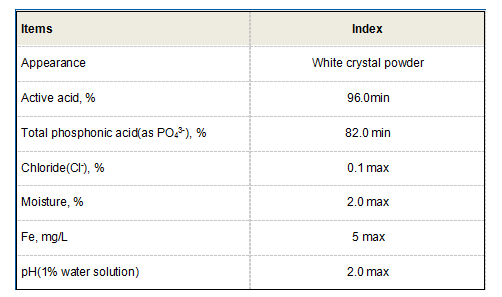
Types of Scale Inhibitors
Scale inhibitors generally fall into several categories based on their chemical composition. Among the most common types are
1. Polyphosphates These compounds work by interfering with the crystallization process of scale-forming minerals, preventing them from depositing on surfaces. 2. Threshold Inhibitors These substances react with scale-forming ions in the water, inhibiting the formation of scale at lower concentrations than would otherwise be possible.
3. Bio-inhibitors In addition to traditional scale inhibitors, some compounds prevent microbial-induced scaling, which can exacerbate scaling issues in cooling and heating systems.
scale and corrosion inhibitor
Types of Corrosion Inhibitors
Similarly, corrosion inhibitors can be categorized based on their chemical structure and mechanism of action
1. Anodic Inhibitors These materials primarily function by forming a protective oxide layer on the surface of the metal, reducing the electrochemical reactions that lead to corrosion.
2. Cathodic Inhibitors These compounds aid in shifting the electrochemical reactions towards the cathode, thereby minimizing corrosion rates.
3. Volatile Corrosion Inhibitors (VCIs) Often used in enclosed environments, VCIs release vapors that condense on metal surfaces, creating a protective layer against moisture and other corrosive agents.
Implementation Best Practices
To effectively manage scaling and corrosion, industries must adopt a systematic approach to inhibitor application. This involves regular monitoring and testing of water chemistry to determine the appropriate inhibitor type and dosage. Additionally, operators should evaluate the compatibility of inhibitors with existing materials and other chemicals used within the system to ensure optimal performance.
Moreover, regular maintenance and inspection of equipment are vital. Early detection of scaling or corrosion allows for timely intervention, minimizing potential damage and optimizing the effectiveness of inhibitors.
Conclusion
As industries continue to face the challenges posed by scale and corrosion, the use of inhibitors becomes increasingly essential. By understanding the properties and functions of these chemical agents, industries can significantly enhance their operational efficiency, reduce costs, and extend the lifespan of their equipment. In a world where resource management is critical, the strategic application of scale and corrosion inhibitors stands as a vital investment in the future of sustainable industrial operations.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





