scale inhibitor
The Importance of Scale Inhibitors in Industrial Applications
Scale formation is a common problem in various industrial processes, particularly those involving water systems. It occurs when dissolved minerals precipitate and accumulate on surfaces, leading to operational inefficiencies, increased maintenance costs, and potential system failures. To mitigate these issues, scale inhibitors are used to prevent the formation and deposition of scale, ensuring smooth operations. This article explores the roles, types, and benefits of scale inhibitors across different industries.
Understanding Scale Formation
Scale primarily consists of calcium carbonate, magnesium carbonate, and other mineral deposits derived from hard water. When water evaporates in industrial processes, these solids concentrate and subsequently crystallize. The accumulation of scale can significantly impair the efficiency of heat exchangers, boilers, and piping systems, obstructing flow and reducing energy transfer effectiveness, which can eventually lead to equipment failure or shutdowns.
Role of Scale Inhibitors
Scale inhibitors are chemical agents designed to interfere with the crystallization process of scale-forming minerals. They achieve this by modifying the way these minerals aggregate, preventing them from forming solid precipitates. By employing scale inhibitors, industries can maintain cleaner systems, reduce maintenance frequency, and enhance the efficiency and longevity of their equipment.
Types of Scale Inhibitors
1. Phosphonates These are widely used due to their effectiveness against calcium carbonate and other mineral scales. Phosphonates work by binding to the minerals and disrupting crystal growth, thus inhibiting scale deposits.
2. Polyacrylates Known for their versatility, polyacrylates can prevent scale in a wide range of pH levels and temperatures. They work by inhibiting nucleation—the initial stage of crystal formation—and dispersing existing particles.
scale inhibitor
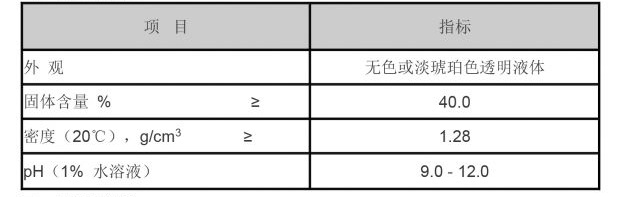
3. Sulfonates These compounds are particularly useful in oil and gas applications, where they not only inhibit scale but also have surfactant properties. Sulfonates can help maintain flow efficiency in pipelines by mitigating deposits.
4. Organic Acids Compounds like citric acid can be effective in dissolving existing scales while also preventing new formations. They are often used in cleaning applications and are biodegradable, making them environmentally friendly choices.
Benefits of Using Scale Inhibitors
The incorporation of scale inhibitors into industrial operations offers a multitude of benefits. First and foremost, they enhance process efficiency by preventing scale-related clogs and obstructions, thus maintaining optimal flow rates and heat transfer. This efficiency translates to energy savings, reducing operational costs and environmental impact.
Moreover, the use of scale inhibitors lessens the frequency and costs associated with maintenance work. Regular cleaning and descaling of equipment can be time-consuming and expensive; by mitigating scale formation, industries can decrease downtime and associated labor costs.
In addition to economic benefits, scale inhibitors contribute to a more sustainable approach to industrial water management. By minimizing water wastage from frequent system purging or equipment failures, industries can operate more sustainably, aligning with modern environmental standards and practices.
Conclusion
In summary, scale inhibitors play a crucial role in enhancing the efficiency and reliability of industrial processes. By understanding the types and functionalities of these chemicals, industries can select appropriate solutions tailored to their needs. The investment in scale inhibitors not only safeguards equipment but also promotes a more sustainable and cost-effective operational model. As industries continue to advance, the importance of scale inhibitors will remain paramount in ensuring smooth and efficient operations in the face of ongoing challenges related to scale formation.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





