Sodium Content in Polyaspartic Acid and Its Implications for Applications
Exploring the Sodium Content of Polyaspartic Acid Applications, Benefits, and Considerations
Polyaspartic acid, a biodegradable polymer derived from the amino acid aspartic acid, has gained attention in various fields due to its unique properties and versatility. Among the most notable aspects of polyaspartic acid is its sodium content, which plays a significant role in its applications, specifically in the formulation of coatings, adhesives, and agricultural products.
Understanding Polyaspartic Acid
Polyaspartic acid is a polyamino acid characterized by its high water solubility, low toxicity, and environmental safety. Its unique structural attributes allow it to form a range of derivatives, influencing its physical and chemical properties. When sodium ions are introduced, specifically in the form of sodium polyaspartate, the polymer's characteristics can be significantly altered, enhancing its functionality in various applications.
Sodium Content Importance and Impact
The sodium content in polyaspartic acid derivatives is an essential factor that influences several properties such as solubility, reactivity, and compatibility with other materials. The presence of sodium enhances the ionic character of polyaspartic acid, resulting in increased solubility in water. This solubility makes sodium polyaspartate an ideal candidate for applications where water-based formulations are preferred, such as in coatings and adhesives.
In agricultural contexts, sodium polyaspartate serves as a biodegradable surfactant, helping to improve the effectiveness of fertilizers and pesticides. Its ability to enhance nutrient uptake and reduce soil erosion demonstrates its potential in sustainable agriculture. Moreover, the sodium component allows for better dispersion of particles, leading to improved performance of agricultural chemicals.
Applications in Coatings and Adhesives
sodium of polyaspartic acid
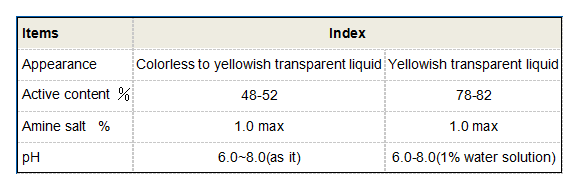
One of the most significant applications of sodium polyaspartate is in the field of coatings. The unique properties imparted by sodium content allow for enhanced adhesion, flexibility, and durability of protective coatings. These coatings are widely used in industries ranging from automotive to construction, providing corrosion resistance and prolonging the lifespan of materials.
Sodium polyaspartate-based adhesives offer advantages over traditional adhesives due to their superior bonding capabilities and lower toxicity. These adhesives can be used in various applications, including woodworking and packaging, where strong, environmentally friendly bonding agents are desired.
Environmental Considerations
The biodegradable nature of polyaspartic acid makes sodium-containing derivatives particularly attractive in an era where environmental sustainability is paramount. Traditional polymers often contribute to pollution and environmental degradation, whereas polyaspartic acid breaks down into non-toxic byproducts. The incorporation of sodium further enhances its performance while minimizing environmental impact.
However, it is essential to monitor the sodium levels in formulations. Excessive sodium can lead to issues such as soil salinization in agricultural applications or undesirable properties in coatings and adhesives. Thus, careful formulation and dosage are crucial to maximizing benefits while mitigating potential drawbacks.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the sodium content of polyaspartic acid derivatives, such as sodium polyaspartate, significantly impacts their performance across various applications. From enhancing solubility and reactivity to contributing to environmentally friendly solutions in coatings, adhesives, and agriculture, sodium polyaspartic acid stands out as a versatile and beneficial material. As industries continue to seek sustainable alternatives, understanding and optimizing the sodium content in polyaspartic acid will be crucial for developing innovative products that meet both performance needs and environmental standards. The future of polyaspartic acid derivatives looks promising, with ongoing research likely to unlock even more potential applications and benefits.
-
Water Treatment with Flocculant Water TreatmentNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polymaleic AnhydrideNewsJun.12,2025
-
Polyaspartic AcidNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with IsothiazolinonesNewsJun.12,2025
-
Enhance Industrial Processes with PBTCA SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025
-
Dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium Chloride SolutionsNewsJun.12,2025





