Effective Water Treatment Solutions Using Flocculants for Enhanced Clarity and Purity
Understanding Water Flocculants Their Role and Importance in Water Treatment
Water treatment is a critical aspect of environmental management, ensuring that we have access to clean and safe water for various purposes, including drinking, agriculture, and industrial applications. One of the essential components of effective water treatment is the use of flocculants. In this article, we will explore the concept of water flocculants, how they work, and their significance in the water treatment process.
What Are Water Flocculants?
Water flocculants are chemical agents used to enhance the aggregation of suspended particles in water, facilitating their removal. These particles can include sediments, mud, algae, and other contaminants that contribute to water turbidity. Flocculants work by neutralizing the charges on these particles, allowing them to clump together or flocculate. The resulting larger particles, or flocs, can then be easily separated from the water, either through sedimentation or filtration.
Flocculants can be categorized into two main types inorganic and organic. Inorganic flocculants, such as aluminum sulfate (alum) and ferric chloride, have been widely used due to their effectiveness and relatively low cost. Organic flocculants, typically synthetic polyacrylamides or natural polymers like starch, offer advantages such as higher efficiency at lower doses and improved performance in specific applications.
The Mechanism of Flocculation
The process of flocculation involves several steps. Initially, rapid mixing is employed to distribute the flocculant evenly throughout the water. This is followed by slow mixing, which allows sufficient time for the flocculant to interact with the suspended particles. As the flocculant binds to the particles, they begin to form larger aggregates. Finally, the water is allowed to settle, and the formed flocs can be easily removed.
water flocculant
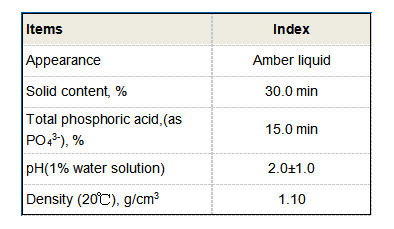
Effective flocculation depends on various factors, including pH, temperature, and the type and concentration of flocculants used. Operators must carefully monitor these parameters to optimize the flocculation process and ensure maximum removal of contaminants.
Benefits of Using Water Flocculants
The incorporation of flocculants in water treatment processes provides several advantages. Firstly, they significantly improve the efficiency of solid-liquid separation. By facilitating the aggregation of particles, flocculants accelerate the sedimentation process, leading to shorter treatment times.
Secondly, using flocculants can enhance water quality. The removal of suspended solids is crucial for reducing turbidity, which not only affects aesthetic quality but can also harbor pathogens and harmful microorganisms. Cleaner water contributes to better health outcomes for communities, especially in regions relying on untreated or poorly treated water sources.
Additionally, flocculants can help reduce the environmental impact of wastewater disposal. By improving the sedimentation of sludge in wastewater treatment plants, flocculants minimize the volume of waste that requires further treatment or disposal, ultimately promoting more sustainable water management practices.
Conclusion
In summary, water flocculants play a vital role in modern water treatment processes. Their ability to enhance particle aggregation leads to improved water quality and efficient treatment outcomes. As we face increasing challenges related to water scarcity and pollution, the continued use and development of effective flocculants will be essential in ensuring access to clean water for all. Understanding the science behind flocculation and its practical applications can help us make informed decisions to safeguard our precious water resources for future generations.
-
Pbtc Scale InhibitorPBTC: A Scale Protector for Industrial Water TreatmentNewsAug.05,2025
-
Organic Phosphonate: An Efficient Defender in the Field of Scale InhibitionNewsAug.05,2025
-
Hydrolyzed Polymaleic Anhydride: Green Pioneer in Scale Inhibition FieldNewsAug.05,2025
-
PAPEMP Polyamino Polyether Methylene Phosphonic Acid For SaleNewsAug.05,2025
-
Flocculant Water Treatment: A Pioneer in Purification in the Field of Water TreatmentNewsAug.05,2025
-
Benzyl Isothiazolinone: An Efficient and Broad-Spectrum Antibacterial Protective GuardNewsAug.05,2025





