Jun . 14, 2024 04:52
Back to list
What is poly aluminum chloride used for?
Poly Aluminum Chloride An Innovative Coagulant in Water Treatment
Water treatment is an essential process that ensures the availability of safe and clean water for human consumption. One of the most critical steps in water treatment is coagulation, which involves the agglomeration of small particles into larger ones that can be easily removed. Poly aluminum chloride (PAC) is an innovative coagulant that has gained popularity in recent years due to its effectiveness and efficiency.
PAC is a synthetic polymer that contains aluminum and chloride ions. It is produced by the reaction of aluminum sulfate and sodium hydroxide in a controlled environment. The resulting product is a highly charged ionic compound that can rapidly neutralize the negative charges on suspended particles in water. This neutralization causes the particles to clump together, forming larger flocs that can be easily separated from the water.
One of the main advantages of using PAC as a coagulant is its ability to work effectively at low temperatures and pH levels. Unlike other coagulants, PAC does not require high temperatures or specific pH levels to perform optimally. This makes it an ideal choice for treating water in cold climates or areas with varying water quality.
Another benefit of PAC is its reduced sludge production compared to traditional coagulants like alum or ferric chloride. Sludge is a byproduct of the coagulation process that must be disposed of properly Sludge is a byproduct of the coagulation process that must be disposed of properly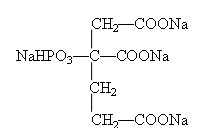 Sludge is a byproduct of the coagulation process that must be disposed of properly Sludge is a byproduct of the coagulation process that must be disposed of properly
Sludge is a byproduct of the coagulation process that must be disposed of properly Sludge is a byproduct of the coagulation process that must be disposed of properly what is poly aluminum chloride. With PAC, the amount of sludge produced is significantly lower, reducing disposal costs and environmental impact.
In addition to its effectiveness as a coagulant, PAC also has disinfectant properties. It can kill bacteria and viruses present in the water, making it suitable for use in wastewater treatment facilities. This dual function makes PAC a cost-effective solution for both water treatment and waste management.
However, there are some drawbacks to using PAC as a coagulant. One potential issue is the presence of residual aluminum in the treated water, which can be harmful if consumed in excess. To address this concern, manufacturers have developed modified versions of PAC that contain less aluminum or alternative coagulants that do not use aluminum.
Despite these challenges, poly aluminum chloride remains a popular choice for water treatment facilities worldwide. Its effectiveness, efficiency, and versatility make it an attractive option for those seeking to improve water quality and protect public health. As research continues on this innovative coagulant, it will undoubtedly play an increasingly vital role in ensuring access to safe and clean water for all.
what is poly aluminum chloride. With PAC, the amount of sludge produced is significantly lower, reducing disposal costs and environmental impact.
In addition to its effectiveness as a coagulant, PAC also has disinfectant properties. It can kill bacteria and viruses present in the water, making it suitable for use in wastewater treatment facilities. This dual function makes PAC a cost-effective solution for both water treatment and waste management.
However, there are some drawbacks to using PAC as a coagulant. One potential issue is the presence of residual aluminum in the treated water, which can be harmful if consumed in excess. To address this concern, manufacturers have developed modified versions of PAC that contain less aluminum or alternative coagulants that do not use aluminum.
Despite these challenges, poly aluminum chloride remains a popular choice for water treatment facilities worldwide. Its effectiveness, efficiency, and versatility make it an attractive option for those seeking to improve water quality and protect public health. As research continues on this innovative coagulant, it will undoubtedly play an increasingly vital role in ensuring access to safe and clean water for all.
 Sludge is a byproduct of the coagulation process that must be disposed of properly Sludge is a byproduct of the coagulation process that must be disposed of properly
Sludge is a byproduct of the coagulation process that must be disposed of properly Sludge is a byproduct of the coagulation process that must be disposed of properly what is poly aluminum chloride. With PAC, the amount of sludge produced is significantly lower, reducing disposal costs and environmental impact.
In addition to its effectiveness as a coagulant, PAC also has disinfectant properties. It can kill bacteria and viruses present in the water, making it suitable for use in wastewater treatment facilities. This dual function makes PAC a cost-effective solution for both water treatment and waste management.
However, there are some drawbacks to using PAC as a coagulant. One potential issue is the presence of residual aluminum in the treated water, which can be harmful if consumed in excess. To address this concern, manufacturers have developed modified versions of PAC that contain less aluminum or alternative coagulants that do not use aluminum.
Despite these challenges, poly aluminum chloride remains a popular choice for water treatment facilities worldwide. Its effectiveness, efficiency, and versatility make it an attractive option for those seeking to improve water quality and protect public health. As research continues on this innovative coagulant, it will undoubtedly play an increasingly vital role in ensuring access to safe and clean water for all.
what is poly aluminum chloride. With PAC, the amount of sludge produced is significantly lower, reducing disposal costs and environmental impact.
In addition to its effectiveness as a coagulant, PAC also has disinfectant properties. It can kill bacteria and viruses present in the water, making it suitable for use in wastewater treatment facilities. This dual function makes PAC a cost-effective solution for both water treatment and waste management.
However, there are some drawbacks to using PAC as a coagulant. One potential issue is the presence of residual aluminum in the treated water, which can be harmful if consumed in excess. To address this concern, manufacturers have developed modified versions of PAC that contain less aluminum or alternative coagulants that do not use aluminum.
Despite these challenges, poly aluminum chloride remains a popular choice for water treatment facilities worldwide. Its effectiveness, efficiency, and versatility make it an attractive option for those seeking to improve water quality and protect public health. As research continues on this innovative coagulant, it will undoubtedly play an increasingly vital role in ensuring access to safe and clean water for all. Share
Latest news
-
Understanding Polycarboxylic Acids: Properties, Applications, and Future PotentialNewsJul.28,2025
-
Scale Inhibitor Explained: How to Protect Your System from Limescale and Hard Water DamageNewsJul.28,2025
-
Scale and Corrosion Inhibitors: Essential Chemicals for Industrial Water System ProtectionNewsJul.28,2025
-
Polyaspartic Acid: A Biodegradable Polymer for Sustainable ChemistryNewsJul.28,2025
-
Isothiazolinones: A Versatile Antimicrobial Class with Industrial Power and Regulatory ChallengesNewsJul.28,2025
-
A Deep Dive into 2-Phosphonobutane-1,2,4-Tricarboxylic Acid (PBTC)NewsJul.28,2025





